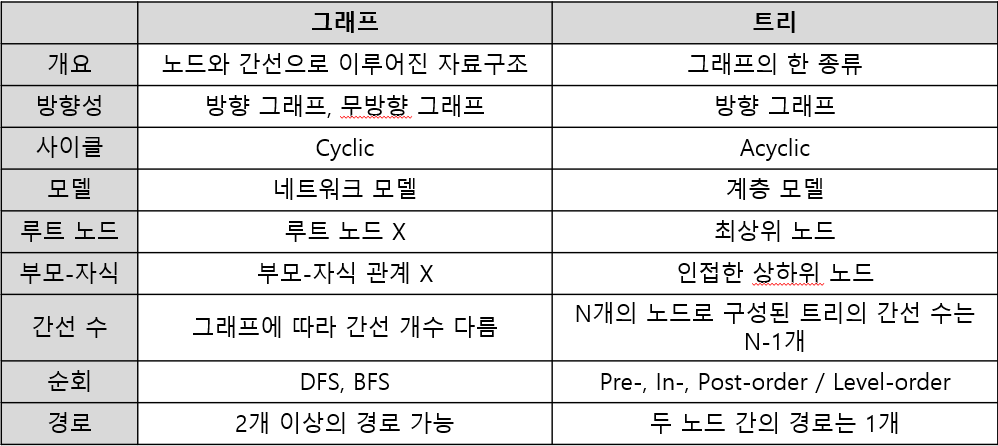
그래프
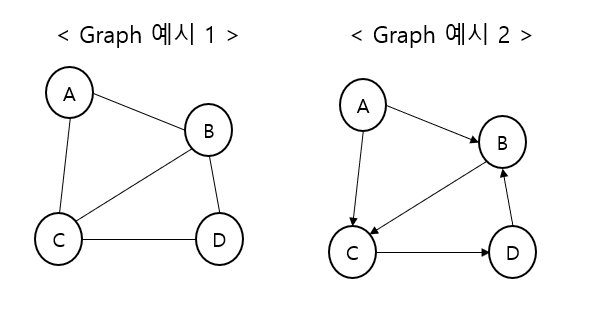
그래프 (Graph)
정점과 간선으로 이루어진 자료구조 (Cyclic)
연결된 정점간의 관계를 표현할 수 있는 자료구조
그래프의 용도
지하철 노선도, 통신 네트워크, …
그래프 구조
정점(Vertex): 각 노드
간선(Edge): 노드와 노드를 연결하는 선 (link, branch)
인접 정점(Adjacent vertex): 간선 하나를 두고 바로 연결된 정점
정점의 차수(Degree):
무방향 그래프에서 하나의 정점에 인접한 정점의 수
무방향 그래프 모든 정점 차수의 합 = 그래프 간선의 수 2배
진입 차수(In-degree): 방향 그래프에서 외부에서 오는 간선의 수
진출 차수(Out-degree): 방향 그래프에서 외부로 나가는 간선의 수
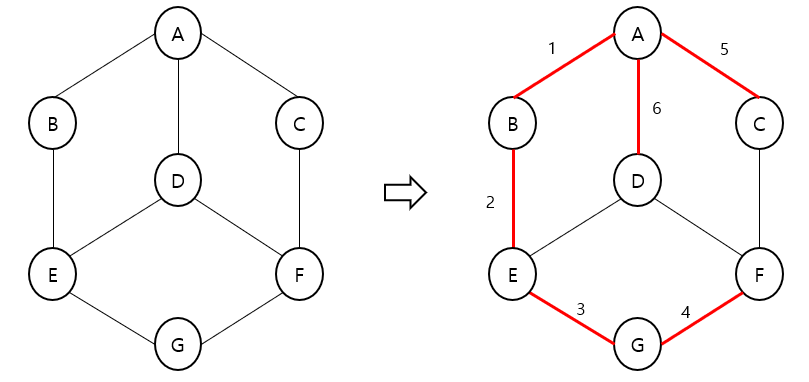
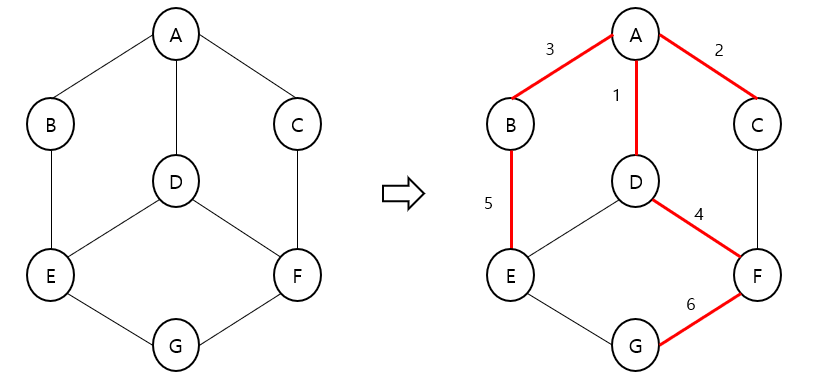
경로 길이(Path length): 경로를 구성하는데 사용된 간선의 수
단순 경로(Simple path): 경로 중에서 반복되는 정점이 없는 경우
사이클(Cycle): 단순 경로의 시작 정점과 끝 정점이 동일한 경우
그래프의 특징과 트리와의 차이
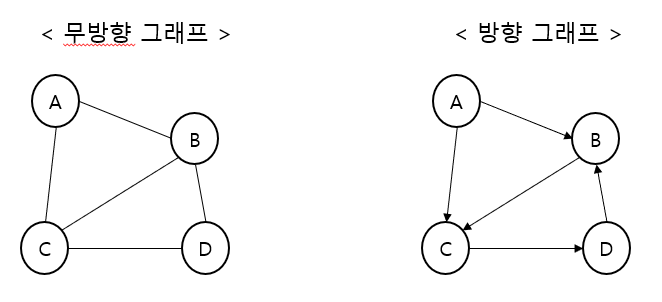
그래프의 종류 (1)
무방향 그래프
간선에 방향이 없는 그래프 (양방향 이동 가능)
정점 A - B 간선의 표현: (A, B) = (B, A)
방향 그래프
간선에 방향이 있는 그래프 (해당 방향으로만 이동 가능)
정점 A → B 간선의 표현: <A, B> ≠ <B, A>
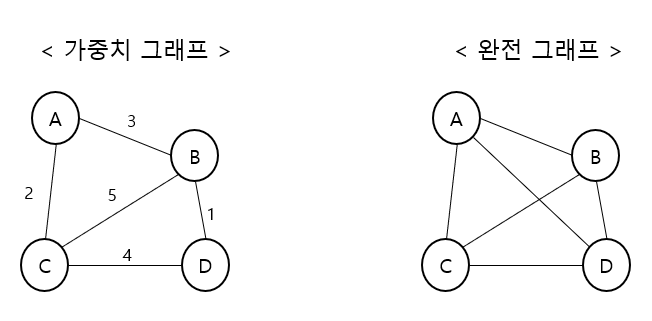
그래프의 종류 (2)
가중치 그래프
간선에 값이 있는 그래프 (이동 비용)
완전 그래프
모든 정점이 서로 연결되어 있는 그래프
정점이 N개일 경우, 간선의 수는 n(n-1)/2 개
그래프 탐색 – DFS
깊이 우선 탐색 (Depth First Search)
각 노드에 방문했는지 여부를 체크할 배열과 스택 이용하여 구현
그래프 탐색 – BFS
너비 우선 탐색 (Breath First Search)
각 노드에 방문했는지 여부를 체크할 배열과 큐 이용하여 구현
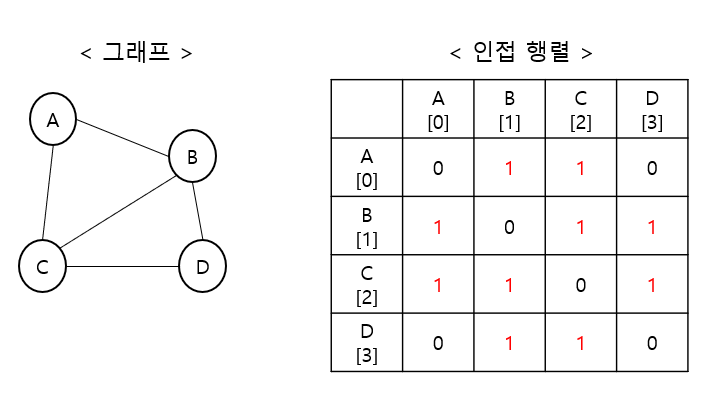
그래프의 구현 (1)
인접 행렬 (Adjacency Matrix)
2차원 배열 이용
인접 행렬의 장단점
간선 정보의 확인과 업데이트가 빠름 O(1)
인접 행렬을 위한 메모리 공간 차지
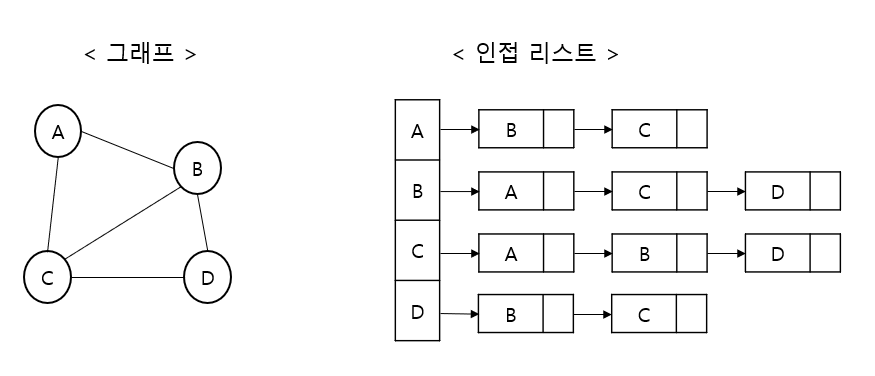
그래프의 구현 (2)
인접 리스트 (Adjacency List)
연결리스트 이용
인접 행렬의 장단점
메모리 사용량이 상대적으로 적고, 노드의 추가 삭제 빠름
간선 정보 확인이 상대적으로 오래 걸림
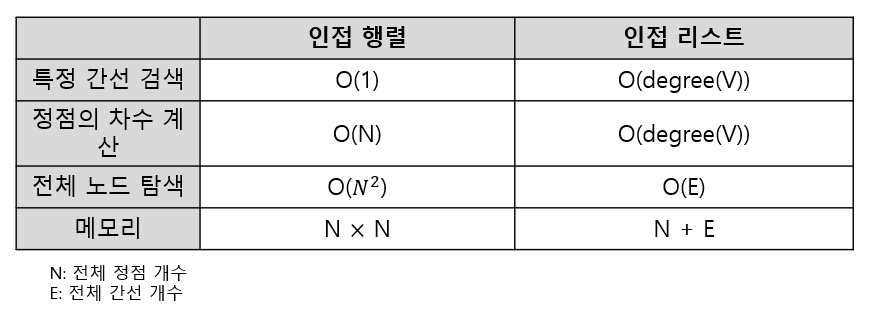
인접 행렬 vs 인접 리스트
인접 행렬
노드의 개수가 적고 간선의 수가 많을 때 유리
인접 리스트
노드의 개수가 많고 간선의 수가 적을 때 유리
비선형 자료구조 - 그래프
인접 행렬을 이용한 그래프 구현
// 비선형 자료구조 - 그래프
// 인접 행렬을 이용한 그래프 구현
class MyGraphMatrix {
char[] vertices;
int[][] adjMat;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphMatrix() {}
public MyGraphMatrix(int size) {
this.vertices = new char[size];
this.adjMat = new int[size][size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(char data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is full!");
return;
}
this.vertices[this.elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 1;
}
public void addDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
}
public void deleteEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 0;
}
public void deleteDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
}
public void printAdjacentMatrix() {
System.out.print(" ");
for (char item: this.vertices) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < this.elemCnt; i++) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[i] + " ");
for (int j = 0; j < this.elemCnt; j++) {
System.out.print(this.adjMat[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyGraphMatrix graph = new MyGraphMatrix(4);
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.printAdjacentMatrix();
}
}
A B C D
A 0 1 1 0
B 1 0 1 1
C 1 1 0 1
D 0 1 1 0
인접 리스트를 이용한 그래프 구현
// Practice1
// 인접 리스트를 이용한 그래프 구현
class Node {
int id;
Node next;
public Node(int id, Node next) {
this.id = id;
this.next = next;
}
}
class MyGraphList {
char vertices[];
Node[] adjList;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphList() {}
public MyGraphList(int size) {
this.vertices = new char[size];
this.adjList = new Node[size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(char data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is full!");
return;
}
this.vertices[elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjList[x] = new Node(y, this.adjList[x]);
this.adjList[y] = new Node(x, this.adjList[y]);
}
public void addDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjList[x] = new Node(y, this.adjList[x]);
}
public void printAdjacentList() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.elemCnt; i++) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[i] + ": ");
Node cur = this.adjList[i];
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[cur.id] + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyGraphList graph = new MyGraphList(4);
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.printAdjacentList();
}
}
A: C B
B: D C A
C: D B A
D: C B
인접 행렬 그래프의 DFS, BFS
// Practice2
// 인접 행렬 그래프의 DFS, BFS
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
class MyGraphMatrix2 extends MyGraphMatrix {
public MyGraphMatrix2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void dfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curId = stack.pop();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
for (int i = this.elemCnt - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (this.adjMat[curId][i] == 1 && visited[i] == false) {
stack.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void bfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curId = queue.poll();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
for (int i = this.elemCnt - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (this.adjMat[curId][i] == 1 && visited[i] == false) {
queue.offer(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyGraphMatrix2 graph = new MyGraphMatrix2(7);
graph.addVertex('A'); // 0
graph.addVertex('B'); // 1
graph.addVertex('C'); // 2
graph.addVertex('D'); // 3
graph.addVertex('E'); // 4
graph.addVertex('F'); // 5
graph.addVertex('G'); // 6
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 4);
graph.addEdge(2, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 4);
graph.addEdge(3, 5);
graph.addEdge(4, 6);
graph.addEdge(5, 6);
graph.dfs(0);
graph.bfs(0);
}
}
A B E G F C D
A D C B F E G
인접 리스트 그래프의 DFS, BFS
// Practice3
// 인접 리스트 그래프의 DFS, BFS
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
class MyGraphList2 extends MyGraphList {
public MyGraphList2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void dfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curId = stack.pop();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
Node cur = this.adjList[curId];
while (cur != null) {
if (visited[cur.id] == false) {
stack.push(cur.id);
visited[cur.id] = true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void bfs(int id) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elemCnt];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curId = queue.poll();
System.out.print(this.vertices[curId] + " ");
Node cur = this.adjList[curId];
while (cur != null) {
if (visited[cur.id] == false) {
queue.offer(cur.id);
visited[cur.id] = true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyGraphList2 graph = new MyGraphList2(7);
graph.addVertex('A'); // 0
graph.addVertex('B'); // 1
graph.addVertex('C'); // 2
graph.addVertex('D'); // 3
graph.addVertex('E'); // 4
graph.addVertex('F'); // 5
graph.addVertex('G'); // 6
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 4);
graph.addEdge(2, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 4);
graph.addEdge(3, 5);
graph.addEdge(4, 6);
graph.addEdge(5, 6);
graph.dfs(0);
graph.bfs(0);
}
}
A B E G F C D
A D C B F E G
문제 풀이
Undirected 그래프에서 center node 를 출력
// Practice1
// Center Node 찾기
// Undirected 그래프에서 center node 를 출력하세요.
// Center node 는 다른 모든 노드와 연결된 노드를 의미
// 다른 모드와 연결된 노드는 하나라고 가정
// 입력 그래프: { {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {4, 2} }
// 출력: 2
// 입력 그래프: { {1,2}, {5,1}, {1,3}, {1,4} }
// 출력: 1
class MyGraphMatrix {
char vertices[];
int[][] adjMat;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphMatrix() {}
public MyGraphMatrix(int size) {
this.vertices = new char[size];
this.adjMat = new int[size][size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(char data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is full!");
return;
}
this.vertices[this.elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 1;
}
public void addDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 1;
}
public void deleteEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
this.adjMat[y][x] = 0;
}
public void deleteDirectedEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjMat[x][y] = 0;
}
public void printAdjacentMatrix() {
System.out.print(" ");
for (char item: this.vertices) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < this.elemCnt; i++) {
System.out.print(this.vertices[i] + " ");
for (int j = 0; j < this.elemCnt; j++) {
System.out.print(this.adjMat[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static int solution(int[][] e) {
MyGraphMatrix graph = new MyGraphMatrix(e.length + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < e.length; i++) {
graph.addEdge(e[i][0] - 1, e[i][1] - 1);
}
int[] edgeCnt = new int[e.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.adjMat.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph.adjMat[i].length; j++) {
if (graph.adjMat[i][j] == 1) {
edgeCnt[i] += 1;
}
}
}
int maxCnt = -1;
int maxIdx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < edgeCnt.length; i++) {
if (maxCnt < edgeCnt[i]) {
maxCnt = edgeCnt[i];
maxIdx = i;
}
}
return maxIdx + 1;
}
public static int solution2(int[][] e) {
return e[0][0] == e[1][0] || e[0][0] == e[1][1] ? e[0][0] : e[0][1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] edges = { {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {4, 2} };
System.out.println(solution(edges));
System.out.println(solution2(edges));
System.out.println();
edges = new int[][]{ {1,2}, {5,1}, {1,3}, {1,4} };
System.out.println(solution(edges));
System.out.println(solution2(edges));
}
}
2
2
1
1
주어진 그래프에서 시작 노드에서 끝 노드로 가는 길이 있는지 확인하는 프로그램
// Practice2
// 주어진 그래프에서 시작 노드에서 끝 노드로 가는 길이 있는지 확인하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// path 가 존재하면 true 없으면 false 출력
// 입력 예시)
// 노드 개수 = 3
// 간선 정보 = { {0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 0} }
// 출발 노드 = 0
// 종착 노드 = 2
// 출력 : true
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
class Node {
int id;
Node next;
public Node(int id, Node next) {
this.id = id;
this.next = next;
}
}
class MyGraphList {
int vertices[];
Node[] adjList;
int elemCnt;
public MyGraphList() {}
public MyGraphList(int size) {
this.vertices = new int[size];
this.adjList = new Node[size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.elemCnt == this.vertices.length;
}
public void addVertex(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Graph is full!");
return;
}
this.vertices[elemCnt++] = data;
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y) {
this.adjList[x] = new Node(y, this.adjList[x]);
this.adjList[y] = new Node(x, this.adjList[y]);
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int dest) {
MyGraphList graph = new MyGraphList(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.addVertex(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
graph.addEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> visitedItem = new ArrayList();
dfs(graph, 0, visitedItem);
if (visitedItem.contains(source) && visitedItem.contains(dest)) {
System.out.println("true");
} else {
System.out.println("false");
}
}
public static void dfs(MyGraphList graph, int id, ArrayList<Integer> visitedItem) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[graph.vertices.length];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(id);
visited[id] = true;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curId = stack.pop();
// 출력 대신 list에 추가
visitedItem.add(curId);
Node cur = graph.adjList[curId];
while (cur != null) {
if (visited[cur.id] == false) {
stack.push(cur.id);
visited[cur.id] = true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int n = 3;
int[][] edges = { {0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 0} };
int source = 0;
int dest = 2;
solution(n, edges, source, dest);
n = 6;
edges = new int[][]{ {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {3, 5}, {5, 4}, {4, 3} };
source = 0;
dest = 5;
solution(n, edges, source, dest);
}
}
true
false
주어진 그래프를 두 개의 그래프로 분리할 수 있는지 확인 하는 프로그램
// Practice3
// 주어진 그래프를 두 개의 그래프로 분리할 수 있는지 확인 하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 분리 조건: 인접하지 않은 노드끼리 분리
// 모든 노드는 연결되어 있다.
// 분리 가능하면 true, 불가능하면 false 출력
// 예시 입력)
// 그래프: { {1, 3}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {0, 2} }
// 출력: true
// 그래프: { {1, 2, 3}, {0, 2}, {0, 1, 3}, {0, 2} }
// 출력: false
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution(int[][] graph) {
int[] flags = new int[graph.length];
if (checkSplit(graph, flags, 1, 0) == true) {
System.out.println("true");
} else {
System.out.println("false");
}
}
public static boolean checkSplit(int[][] graph, int[] flags, int flag, int node) {
if (flags[node] != 0) {
return flags[node] == flag;
}
flags[node] = flag;
for (int adjacentNode : graph[node]) {
if (!checkSplit(graph, flags, -flag, adjacentNode)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] graph = { {1, 3}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {0, 2} };
solution(graph);
graph = new int[][]{ {1, 2, 3}, {0, 2}, {0, 1, 3}, {0, 2} };
solution(graph);
}
}
true
false
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment