기초수학 연습 문제 풀이1
문제 설명
파스칼의 삼각형(Pascal’s triangle)은 수학에서 이항계수를 삼각형 모양의 기하학적 형태로 배열한 것이다.
파스칼의 삼각형은 다음과 같이 만들 수 있다:
- 첫 번째 줄에는 숫자 1을 쓴다.
- 그 다음 줄은 바로 위의 왼쪽 숫자와 오른쪽 숫자를 더한다.
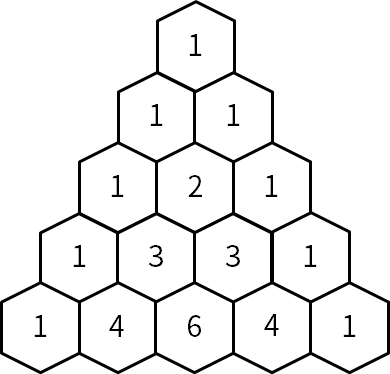
삼각형의 행의 수가 입력으로 주어졌을 때,
파스칼의 삼각형을 출력하시오.
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1 | [[1]] |
| 3 | [[1], [1, 1], [1, 2, 1]] |
| 5 | [[1], [1, 1], [1, 2, 1], [1, 3, 3, 1], [1, 4, 6, 4, 1]] |
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice1 {
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> solution(int numRows) {
// ArrayList 의 ArrayList
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
if(j == 0 || j == i) {
list.add(1);
}
else {
// 하나 위의 행의 좌, 우 데이터 합하기
int x = result.get(i - 1).get(j - 1);
int y = result.get(i - 1).get(j);
list.add(x + y);
}
}
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution(1));
System.out.println(solution(2));
System.out.println(solution(3));
System.out.println(solution(4));
System.out.println(solution(5));
}
}
[[1]]
[[1], [1, 1]]
[[1], [1, 1], [1, 2, 1]]
[[1], [1, 1], [1, 2, 1], [1, 3, 3, 1]]
[[1], [1, 1], [1, 2, 1], [1, 3, 3, 1], [1, 4, 6, 4, 1]]
문제 설명
주어진 arr 배열은 양의 정수로 구성되어 있습니다. 이 배열을 사용하여 다음 조건을 만족하는 permutation을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- 현재 데이터보다 이전의 큰 수를 출력합니다.
- 한 번의 swap으로 출력 가능한 가장 큰 수를 출력합니다.
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 3, 2, 1 | 3, 1, 2 |
| 1, 9, 4, 7, 6 | 1, 9, 4, 6, 7 |
| 1, 1, 2, 3 | 1, 1, 2, 3 |
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
// 현재 데이터의 정렬 상태 확인
// swap 필요 index 세팅
int idx = -1;
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
if (arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) {
idx = i - 1;
break;
}
}
// idx 가 -1 이면 기 정렬 상태
if (idx == -1) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
return;
}
// 바꿀 자리 찾아서 swap
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > idx; i--) {
if (arr[i] < arr[idx] && arr[i] != arr[i - 1]) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[idx];
arr[idx] = tmp;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {3, 2, 1};
solution(arr);
arr = new int[]{1, 9, 4, 7, 6};
solution(arr);
arr = new int[]{1, 1, 2, 3};
solution(arr);
}
}
[3, 1, 2]
[1, 9, 4, 6, 7]
[1, 1, 2, 3]
문제 설명
주어진 문자열 s1과 s2가 있습니다.
s1의 순열(permutation)이 s2의 부분 문자열(substring)인 경우에는 true를 반환하고, 그렇지 않은 경우에는 false를 반환하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
입출력 예시
s1 |
s2 |
출력 |
|---|---|---|
| “ab” | “adbak” | true |
| “ac” | “car” | true |
| “ak” | “aabbkk” | false |
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice3 {
// # 1 기본 permutation 방법
public static boolean solution(String s1, String s2) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[s1.length()];
char[] out = new char[s1.length()];
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
permutation(s1.toCharArray(), 0, s1.length(), s1.length(), visited, out, list);
for (String s: list) {
if (s2.contains(s)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 기존 permutation 코드 문제에 맞춰 변형
public static void permutation(char[] arr, int depth, int n, int r, boolean[] visited, char[] out, ArrayList<String> list) {
if (depth == r) {
list.add(new String(out));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true;
out[depth] = arr[i];
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r, visited, out, list);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
// # 2 문제 규칙 찾아 해결
public static boolean solution2(String s1, String s2) {
final int ALPHABET = 26;
// s1 이 s2 보다 긴 경우 s1 으로 permutation 하여 s2 의 부분이 될 수 없으므로 false 반환
if (s1.length() > s2.length()) {
return false;
}
// s1 알파벳별 개수 카운팅
int[] cnt = new int[ALPHABET];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
cnt[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length(); i++) {
// s2 에 해당하는 알파벳 위치 카운트 감소
cnt[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
// s1 의 길이를 넘어선 경우, on/off 형태로 체크
if (i - s1.length() >= 0) {
cnt[s2.charAt(i - s1.length()) - 'a']++;
}
// 카운트 배열이 모두 0 이면 permutation 으로 만들 수 있는 부분 문자열이 있음
boolean isZero = true;
for (int j = 0; j < ALPHABET; j++) {
if (cnt[j] != 0) {
isZero = false;
break;
}
}
if (isZero) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String s1 = "ab";
String s2 = "adbak";
System.out.println(solution(s1, s2));
System.out.println(solution2(s1, s2));
System.out.println();
s1 = "ac";
s2 = "car";
System.out.println(solution(s1, s2));
System.out.println(solution2(s1, s2));
System.out.println();
s1 = "ak";
s2 = "aabbkk";
System.out.println(solution(s1, s2));
System.out.println(solution2(s1, s2));
}
}
true
true
true
true
false
false
문제 설명
주어진 양의 정수가 행복한 수인지 판별하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
행복한 수는 각 자리수를 제곱한 것을 더하는 과정을 반복했을 때 1로 끝나는 수입니다. 행복한 수가 아니라면 1에 도달하지 못하고 같은 수열이 반복됩니다.
‘행복한 수’를 찾는 과정 예시:
19를 확인하는 과정
1^2 + 9^2 = 82
8^2 + 2^2 = 68
6^2 + 8^2 = 100
1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 19 | true |
| 2 | false |
| 61 | false |
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Practice4 {
// 수열 반복 특성을 이용해 해결하는 문제
public static boolean solution(int n) {
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
// HashSet 에 데이터 추가 성공하면 true 반환, 실패하면 false 반환
// 반복되는 수열이 등장할 때 false 로 인해 while 문 종료
while (set.add(n)) {
int squareSum = 0;
// 각 자리수 제곱의 합
while (n > 0) {
int remain = n % 10;
squareSum += remain * remain;
n /= 10;
}
// 1에 도달하면 true 반환
if (squareSum == 1) {
return true;
} else {
n = squareSum;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution(19));
System.out.println(solution(2));
System.out.println(solution(61));
}
}
true
false
false
문제 설명
영토에 대한 지도 정보가 row x col 그리드 형태로 주어졌습니다.
여기서 grid[i][j]가 1이면 땅 영역을 나타내고,
grid[i][j]가 0이면 물 영역을 나타냅니다.
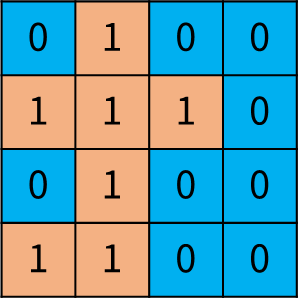
주어진 지도 정보에 따라, 땅의 둘레를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- 각 셀의 변의 길이는 1입니다.
- 지도에는 하나의 독립된 영토만 있습니다. (분리된 땅이 없음)
- 땅 내부에는 물이 존재하지 않습니다.
입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| { {1} } | 4 |
| { {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0, 0} } | 16 |
public class Practice5 {
public static int solution(int[][] grid) {
// 이동 방향
int[][] directions = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
int cnt = 0;
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
// 땅일 때 각 방향 탐색
for (int[] d : directions) {
int x = i + d[0];
int y = j + d[1];
// 최외곽 부분에 닿을 때와 물의 영역에 닿을 때 둘레 카운트 늘려줌
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] == 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
// 재귀 풀이
public static int solution2(int[][] grid) {
int[][] directions = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
// 땅인 경우 각 방향 탐색을 재귀호출로 수행
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
return recursion(grid, directions, i, j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public static int recursion(int[][] grid, int[][] directions, int i, int j) {
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
// 재방문에 의한 중복 계산을 하지 않게 설정
grid[i][j] = -1;
int cnt = 0;
for (int[] d : directions) {
int x = i + d[0];
int y = j + d[1];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] == 0) {
cnt++;
} else {
// 재귀 호출
if (grid[x][y] == 1) {
cnt += recursion(grid, directions, x, y);
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] grid = 1;
System.out.println(solution(grid));
System.out.println(solution2(grid));
System.out.println();
grid = new int[][]{ {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0, 0} };
System.out.println(solution(grid));
System.out.println(solution2(grid));
}
}
4
4
16
16
예제 설명
directions 배열의 각 원소는 [x 방향 이동, y 방향 이동]을 나타냅니다.
{0, 1}: 아래로 이동
{1, 0}: 오른쪽으로 이동
{-1, 0}: 왼쪽으로 이동
{0, -1}: 위로 이동
탐색 과정 예제
예를 들어, grid = { {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0, 0} }에 대해 탐색을 진행해보겠습니다.
i = 0, j = 1 (첫 번째 땅 셀)
현재 좌표 (0, 1)에서 네 방향을 탐색합니다.
for (int[] d : directions) {
int x = 0 + d[0];
int y = 1 + d[1];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] == 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
d = {0, 1}: (0, 2) 탐색 - 물 (cnt 증가)
d = {1, 0}: (1, 1) 탐색 - 땅 (cnt 증가하지 않음)
d = {-1, 0}: (-1, 1) 탐색 - 경계 바깥 (cnt 증가)
d = {0, -1}: (0, 0) 탐색 - 물 (cnt 증가)
이 경우, cnt는 3 증가합니다.
i = 1, j = 0 (다음 땅 셀)
현재 좌표 (1, 0)에서 네 방향을 탐색합니다.
for (int[] d : directions) {
int x = 1 + d[0];
int y = 0 + d[1];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] == 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
d = {0, 1}: (1, 1) 탐색 - 땅 (cnt 증가하지 않음)
d = {1, 0}: (2, 0) 탐색 - 물 (cnt 증가)
d = {-1, 0}: (0, 0) 탐색 - 물 (cnt 증가)
d = {0, -1}: (1, -1) 탐색 - 경계 바깥 (cnt 증가)
이 경우, cnt는 3 증가합니다.
이 과정을 모든 땅 셀에 대해 반복하여, 땅의 둘레를 구할 수 있습니다.
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment