기초수학 연습 문제 풀이2
문제 설명
카탈랑 수는 0번, 1번, 2번, … 순으로 아래와 같이 구성되는 수열을 의미합니다.
- 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, …
이를 점화식으로 나타내면 아래와 같습니다.
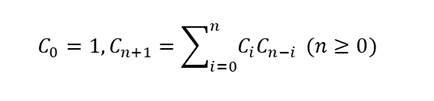
카탈랑 수의 n 번째 값을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
입력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 42 |
| 7 | 429 |
public class Practice1 {
public static int solution(int n) {
int result = 0;
// 0항과 1항은 1
if (n <= 1) {
return 1;
}
// 점화식에 따른 재귀함수 구성
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result += solution(i) * solution(n - i - 1);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution(0));
System.out.println(solution(2));
System.out.println(solution(5));
System.out.println(solution(7));
}
}
1
2
42
429
문제 설명
회문 또는 팰린드롬(palindrome)은 앞 뒤 방향으로 같은 순서의 문자로 구성된 문자열을 말합니다.
- 예시) ‘abba’ ‘kayak’, ‘madam’
유사회문은 문자열 그 자체는 회문이 아니지만 한 문자를 삭제하면 회문이 되는 문자열을 말합니다.
- 예시) ‘summuus’의 5번째 또는 6번째 문자 ‘u’를 제거하면 ‘summus’인 회문을 만들 수 있습니다.
주어진 문자열을 확인한 후 문자열 종류에 따라 다음과 같이 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- 회문: 0
- 유사회문: 1
- 기타: 2
입력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| abba | 0 |
| summuus | 1 |
| xabba | 1 |
| xabbay | 2 |
| comcom | 2 |
| comwwmoc | 0 |
| comwwtmoc | 1 |
public class Practice2 {
public static int solution(String str) {
return isPalindrome(0, str.length() - 1, str.toCharArray(), 0);
}
public static int isPalindrome(int left, int right, char[] arr, int delCnt) {
while (left < right) {
if (arr[left] != (arr[right])) {
// 좌우 값이 동일하지 않은 경우 유사회문인지 아닌지 판단
// 문자 한개 삭제 전이면
if (delCnt == 0) {
// left 를 한칸 오른쪽 또는 right 를 한칸 왼쪽으로 이동 시켜 회문인지 판단
// 회문이면 유사회문 이므로 1 반환 아니면 2 반환
if (isPalindrome(left + 1, right, arr, 1) == 0 ||
isPalindrome(left, right - 1, arr, 1) == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return 2;
}
} else {
// 문자 한개 삭제 후에 다시 이곳에 오면 2 반환
return 2;
}
} else {
// 좌우가 같은 경우에는 left, right index 한 칸씩 이동
left++;
right--;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String[] str = {"abba", "summuus", "xabba", "xabbay", "comcom", "comwwmoc", "comwwtmoc"};
System.out.println(solution("abba"));
System.out.println(solution("summuus"));
System.out.println(solution("xabba"));
System.out.println(solution("xabbay"));
System.out.println(solution("comcom"));
System.out.println(solution("comwwmoc"));
System.out.println(solution("comwwtmoc"));
}
}
0
1
1
2
2
0
1
문제 설명
주어진 1차 방정식에 대해 풀이를 하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
해당 방정식은 ‘+’, ‘-‘, ‘x’ 와 ‘상수’로만 이루어져 있습니다.
해가 없으면 “No solution” 을 출력하고,
해가 무한대인 경우 “Infinite solutions” 를 출력하며,
해가 있는 경우 x의 값을 “x=” 형태로 출력합니다.
입력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| “x+5-3+x=6+x-2” | “x=2” |
| “x=x” | “Infinite solutions” |
| “2x=x” | “x=0” |
public class Practice3 {
public static String solution(String equation) {
String[] parts = equation.split("=");
int[] leftSide = evaluate(parts[0]);
int[] rightSide = evaluate(parts[1]);
// int[] leftSide = evaluate2(parts[0]);
// int[] rightSide = evaluate2(parts[1]);
if (leftSide[0] == rightSide[0] && leftSide[1] == rightSide[1]) {
return "Infinite solutions";
} else if (leftSide[0] == rightSide[0]) {
return "No solution";
}
return "x=" + (rightSide[1] - leftSide[1]) / (leftSide[0] - rightSide[0]);
}
public static int[] evaluate(String str) {
// [0] 에는 x 의 계수, [1] 에는 상수항
int[] result = new int[2];
// # 1
boolean isMinus = false;
int idx = 0;
while (idx != str.length()) {
char c = str.charAt(idx++);
if (c == '+') {
continue;
}
if (c == '-') {
isMinus = true;
continue;
}
if (c == 'x') {
// x 인 경우 부호에 따라 계수 쪽 업데이트
result[0] += isMinus ? -1 : 1;
} else {
// 숫자인 경우
// 그 다음이 x 인 경우 x 의 계수 부분 업데이트
if (idx < str.length() && str.charAt(idx) == 'x') {
result[0] += isMinus ? -(c - '0') : (c - '0');
idx++;
} else {
// 숫자만 있는 경우 상수항 업데이트
result[1] += isMinus ? -(c - '0') : (c - '0');
}
}
isMinus = false;
}
return result;
}
// # 2 정규표현식 사용
public static int[] evaluate2(String str) {
int[] result = new int[2];
// + 또는 -는 포함하여 파싱
for (String s : str.split("(?=[+-])")) {
if (s.equals("+x") || s.equals("x")) {
result[0]++;
} else if (s.equals("-x")) {
result[0]--;
} else if (s.contains("x")) {
result[0] += Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0, s.length() - 1));
} else {
result[1] += Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String equation = "x+5-3+x=6+x-2";
System.out.println(solution(equation));
equation = "x=x";
System.out.println(solution(equation));
equation = "2x=x";
System.out.println(solution(equation));
}
}
x=2
Infinite solutions
x=0
문제 설명
아래와 같이 구성되는 수를 좋은 수라고 합니다.
- 짝수 인덱스 위치에는 짝수
- 홀수 인덱스 위치에는 소수 (2, 3, 5, 7)
- 인덱스는 0 부터 시작합니다.
예를 들면,
2582 는 좋은 수입니다.
- 짝수 인덱스 위치에는 짝수인 2와 8로, 홀수 위치에는 소수인 5와 2로 구성됩니다.
그러나,
3245 는 좋은 수가 아닙니다.
- 짝수 인덱스 위치에 홀수인 3이 위치하고 있습니다.
1 이상의 정수 n이 주어졌을 때, n 자리로 구성될 수 있는 좋은 수의 개수를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
단, n의 값에 따라 값이 클 수 있으므로 결과는 (10^9 + 7)로 나머지 연산을 한 결과로 출력하시오.
입력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 100 |
| 4 | 400 |
| 50 | 564908303 |
public class Practice4 {
// 문제에서 overflow 방지 용으로 주어진 수
final static int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
public static int solution(long n) {
// 5c1 * 4c1 * 5c1 * 4c1 * ...
// 5c1 자리 만큼 * 4c1 자리 만큼 재귀로 계산
return (int) (recursion(5, (n + 1) / 2) * recursion(4, n / 2) % mod);
}
public static long recursion(long x, long y) {
if (y == 0) {
return 1;
}
long p = recursion(x, y / 2);
return p * p * (y % 2 > 0 ? x : 1) % mod;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution(1));
System.out.println(solution(2));
System.out.println(solution(3));
System.out.println(solution(4));
System.out.println(solution(50));
}
}
5
20
100
400
564908303
문제 설명
하노이의 탑은 퍼즐의 일종입니다.
 (Fig. 1. Tower of Hanoi from: wikipedia)
(Fig. 1. Tower of Hanoi from: wikipedia)
하노이의 탑 퍼즐 게임 규칙은 다음과 같습니다.
- 한 번에 한 개의 원판만 옮길 수 있습니다.
- 큰 원판이 작은 원판 위에 있어서는 안 됩니다.
원판의 개수 n이 주어졌을 때
가장 왼쪽 기둥으로부터 끝 기둥으로 이동하는 과정에 대해 출력하는 프로그램을 구현하세요.
입력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 2 | 1 2 1 3 2 3 |
| 3 | 1 3 1 2 3 2 1 3 2 1 2 3 1 3 |
public class Practice5 {
static StringBuffer sb;
public static void solution(int n) {
sb = new StringBuffer();
// 원판 수, 시작 위치, 중간 위치, 끝 위치
hanoi(n, 1, 2, 3);
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void hanoi(int n, int start, int mid, int to) {
if (n == 1) {
// 원판 이동
sb.append(start + " " + to + "\n");
return;
}
// n-1 번 째 원판을 start -> mid 쪽으로 이동 재귀 호출
// 결국 가장 위에 있는 원판 부터 이동 시작
hanoi(n - 1, start, to, mid);
// 위에서 원판 이동 후 다음 원판은 다른 위치로 이동
sb.append(start + " " + to + "\n");
// n-1 번 째 원판을 mid -> to 로 이동
hanoi(n - 1, mid, start, to);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution(2);
System.out.println();
solution(3);
System.out.println();
solution(4);
}
}
1 2
1 3
2 3
1 3
1 2
3 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
1 3
1 2
1 3
2 3
1 2
3 1
3 2
1 2
1 3
2 3
2 1
3 1
2 3
1 2
1 3
2 3
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment