배열
배열 (Array)
많은 수의 데이터를 다룰 때 사용하는 자료구조
각 데이터를 인덱스와 1:1 대응하도록 구성
데이터가 메모리 상에 연속적으로 저장됨
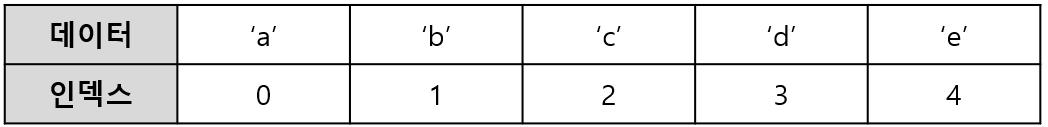
배열의 장점
인덱스를 이용하여 데이터에 빠르게 접근 가능
배열의 단점
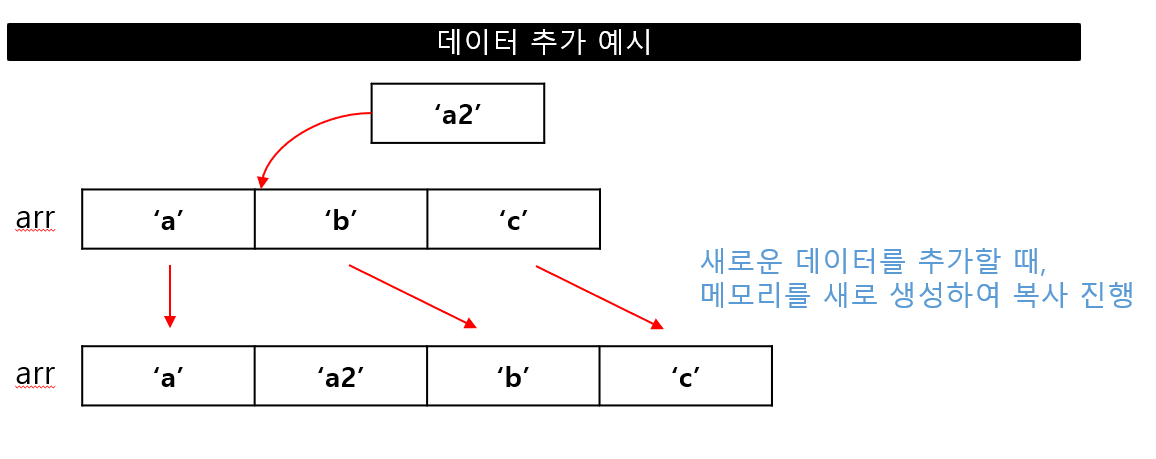
데이터의 추가/삭제가 번거로운 편
미리 최대 길이를 정해서 생성해야 함
가변 길이 배열은 배열의 크기를 변경할 때마다 새로운 배열을 생성
데이터 삭제 시, 인덱스를 유지하기 위해 빈 공간 유지
// 선형 자료구조 - 배열
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1차원 배열
System.out.println("== 1차원 배열 ==");
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int item: arr) {
System.out.println("item = " + item);
}
arr[1] = 100;
System.out.println("arr = " + arr);
// 2차원 배열
System.out.println("== 2차원 배열 ==");
int[][] arr2 = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6} };
System.out.println(arr2[0][1]);
for(int[] row: arr2) {
for(int item: row) {
System.out.println("item = " + item);
}
}
// ArrayList - 1차원, 2차원
System.out.println("== ArrayList ==");
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(5);
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
list1.remove(2);
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
list1.remove(Integer.valueOf(2));
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
ArrayList list2d = new ArrayList();
ArrayList list1d1 = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
ArrayList list1d2 = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(4, 5, 6));
list2d.add(list1d1);
list2d.add(list1d2);
System.out.println("list1d1 = " + list1d1);
System.out.println("list1d2 = " + list1d2);
System.out.println("list2d = " + list2d);
}
}
== 1차원 배열 ==
item = 1
item = 2
item = 3
item = 4
item = 5
arr = [I@6d03e736
== 2차원 배열 ==
2
item = 1
item = 2
item = 3
item = 4
item = 5
item = 6
== ArrayList ==
list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
list1 = [1, 2, 4, 5]
list1 = [1, 4, 5]
list1d1 = [1, 2, 3]
list1d2 = [4, 5, 6]
list2d = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
// Practice
// 기본 배열 자료형을 이용한 배열의 생성, 삽입, 삭제 기능 구현
import java.util.Arrays;
class MyArray {
int[] arr;
// 배열의 초기 사이즈 설정
MyArray(int size) {
this.arr = new int[size];
}
// 배열에 데이터 삽입
public void insertData(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.arr.length) {
System.out.println("Index Error");
return;
}
int[] arrDup = this.arr.clone();
this.arr = new int[this.arr.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
this.arr[i] = arrDup[i];
}
for (int i = index + 1; i < this.arr.length; i++) {
this.arr[i] = arrDup[i - 1];
}
this.arr[index] = data;
}
// 배열에서 특정 데이터 삭제
public void removeData(int data) {
int targetIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < this.arr.length; i++) {
if (this.arr[i] == data) {
targetIndex = i;
break;
}
}
if (targetIndex == -1) {
System.out.println("해당 데이터가 없습니다.");
}
else {
int[] arrDup = this.arr.clone();
this.arr = new int[this.arr.length - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < targetIndex; i++) {
this.arr[i] = arrDup[i];
}
for (int i = targetIndex; i < this.arr.length; i++) {
this.arr[i] = arrDup[i + 1];
}
}
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int size = 5;
MyArray myArray = new MyArray(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
myArray.arr[i] = i + 1;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
myArray.arr[0] = 10;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [10, 2, 3, 4, 5]
myArray.insertData(2, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [10, 2, 20, 3, 4, 5]
myArray.insertData(6, 60);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [10, 2, 20, 3, 4, 5, 60]
myArray.insertData(-1, 0); // Index Error
myArray.removeData(4);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [10, 2, 20, 3, 5, 60]
myArray.removeData(5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myArray.arr)); // [10, 2, 20, 3, 60]
myArray.removeData(99); // 해당 데이터가 없습니다.
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[10, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[10, 2, 20, 3, 4, 5]
[10, 2, 20, 3, 4, 5, 60]
Index Error
[10, 2, 20, 3, 5, 60]
[10, 2, 20, 3, 60]
해당 데이터가 없습니다.
// Practice1
// 배열 arr 의 모든 데이터에 대해서,
// 짝수 데이터들의 평균과 홀수 데이터들의 평균을 출력하세요.
// 입출력 예시)
// 배열 arr: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
// 결과:
// 짝수 평균: 5.0
// 홀수 평균: 5.0
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
float sumEven = 0;
float sumOdd = 0;
int evenCnt = 0;
int oddCnt = 0;
for (int item: arr) {
if (item % 2 == 0) {
sumEven += item;
evenCnt++;
} else {
sumOdd += item;
oddCnt++;
}
}
System.out.println("짝수 평균: " + sumEven / evenCnt);
System.out.println("홀수 평균: " + sumOdd / oddCnt);
}
}
짝수 평균: 5.0
홀수 평균: 5.0
// Practice2
// 배열 arr 에서 target 에 해당하는 값의 인덱스를 출력
// 해당 값이 여러 개인 경우 가장 큰 인덱스 출력
// 입출력 예시)
// 배열 arr: 1, 1, 100, 1, 1, 1, 100
// 결과: 6
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 1, 100, 1, 1, 1, 100};
int target = 100;
int idxMax = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
if (i > idxMax) {
idxMax = i;
}
}
}
if (idxMax >= 0) {
System.out.println(idxMax);
}
}
}
6
// Practice3
// 배열 arr 의 데이터 순서를 거꾸로 변경하세요.
// 추가 배열을 사용하지 않고 구현
// 입출력 예시)
// arr: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
// 결과: 9, 7, 5, 3, 1
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length / 2; i++) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[arr.length - 1 - i];
arr[arr.length - 1 - i] = tmp;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
[9, 7, 5, 3, 1]
// Practice4
// 배열 arr 에서 peek 값 모두 출력
// 입출력 예시)
// arr: 3, 1, 2, 6, 2, 2, 5, 1, 9, 10, 1, 11
// 결과: 3, 6, 5, 10, 11
public class Practice4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 1, 2, 6, 2, 2, 5, 1, 9, 10, 1, 11};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i == 0 && arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
} else if (i == arr.length - 1 && arr[i] > arr[i - 1]){
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
} else {
if (arr[i] > arr[i - 1] && arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
3 6 5 10 11
// Practice5
// 배열 arr 의 값을 오름차순으로 출력
// 입출력 예시)
// arr: 5, 3, 1, 4, 6, 1
// 결과: 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
public class Practice5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5, 3, 1, 4, 6, 1}; // -> 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
int[] visited = new int[arr.length];
int visitCnt = 0;
int minVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minIdx = -1;
while (visitCnt < arr.length) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < minVal && visited[i] == 0) {
minVal = arr[i];
minIdx = i;
}
}
if (minIdx != -1) {
System.out.print(minVal + " ");
visited[minIdx] = 1;
visitCnt++;
}
minVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
minIdx = -1;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1 1 3 4 5 6
// Practice6
// 배열 arr 에서 중복 값을 제거한 새 배열을 만드시오.
// 입출력 예시)
// arr: 1, 5, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 4, 1, 2, 3, 5
// 결과: 1, 5, 3, 2, 4
public class Practice6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 5, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 4, 1, 2, 3, 5};
int[] arrResult = new int[arr.length];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
boolean dupFlag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
if (arr[i] == arrResult[j]) {
dupFlag = true;
}
}
if (dupFlag == false) {
arrResult[cnt++] = arr[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
System.out.print(arrResult[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1 5 3 2 4
// Practice7
// 2차원 배열 arr 을 시계방향 90도 회전시킨 결과를 출력하세요.
// 입출력 예시:
// arr:
// 1 2 3 4 5
// 6 7 8 9 10
// 11 12 13 14 15
// 결과:
// 11 6 1
// 12 7 2
// 13 8 3
// 14 9 4
// 15 10 5
public class Practice7 {
static void printArr(int[][] arr) {
for (int[] item1D: arr) {
for (int item: item1D) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = { {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, {11, 12, 13, 14, 15} };
int[][] arr90 = new int[arr[0].length][arr.length];
printArr(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
int r = arr.length - 1 - i;
arr90[j][r] = arr[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("== After ==");
printArr(arr90);
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
== After ==
11 6 1
12 7 2
13 8 3
14 9 4
15 10 5
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment