선형 자료구조 연습문제
문제 설명
과거에 하기의 modification 함수를 이용해 배열 내 데이터 순서를 변경했었다.
- 최근에 이 변경한 데이터들을 다시 원래의 배열 순서로 변경해야 하는 일이 생겼다.
- 아래의 modification 코드를 분석 후 되돌리는 코드를 작성하세요.
public static int[] modification(int[] arr) {
int[] arrNew = new int[arr.length];
int idx = 0;
int cnt = 0;
int val = arr[idx];
while (cnt < arr.length) {
while (val == 0) {
idx = (idx + 1) % arr.length;
val = arr[idx];
}
arrNew[cnt++] = val;
arr[idx] = 0;
idx = (val + idx) % arr.length;
val = arr[idx];
}
return arrNew;
}
Modification 당시 입출력 샘플
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1 3 5 7 9 | 1 3 7 9 5 |
| 3 6 8 2 | 3 2 6 8 |
되돌리기 입출력 예시
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1 3 7 9 5 | 1 3 5 7 9 |
| 3 2 6 8 | 3 6 8 2 |
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Practice1 {
public static int[] solution(int[] arr){
int[] arrNew = new int[arr.length];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(arrNew[index] == 0) {
break;
}
index = (index + 1) % arr.length;
}
arrNew[index] = arr[i];
index = (index + arr[i]) % arr.length;
}
return arrNew;
}
public static int[] modification(int[] arr) {
int[] arrNew = new int[arr.length];
int idx = 0;
int cnt = 0;
int val = arr[idx];
while (cnt < arr.length) {
while (val == 0) {
idx = (idx + 1) % arr.length;
val = arr[idx];
}
arrNew[cnt++] = val;
arr[idx] = 0;
idx = (val + idx) % arr.length;
val = arr[idx];
}
return arrNew;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
// Modification test
int[] arr = {1, 3, 7, 9, 5};
int[] arrNew = modification(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrNew));
// Revert data
arr = new int[]{1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int[] arrOrigin = solution(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrOrigin));
arr = new int[]{3, 2, 6, 8};
arrOrigin = solution(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrOrigin));
}
}
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
[1, 3, 7, 9, 5]
[3, 6, 8, 2]
문제 설명
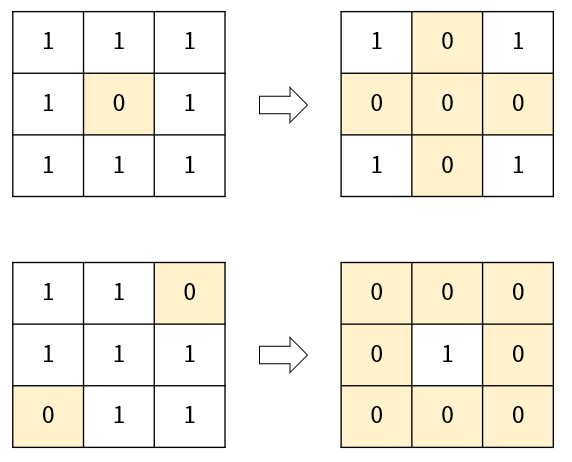
정수로 이루어진 M x N 행렬 데이터가 있다고 하자.
- 행렬의 원소 중에 0이 있을 경우 해당 원소가 위치하는 행과 열 전체 데이터를 0으로 변경하는 코드를 작성하세요.
입출력 예시
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(int[][] matrix) {
boolean frZero = false;
boolean fcZero = false;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
if (i == 0) {
frZero = true;
}
if (j == 0) {
fcZero = true;
}
matrix[i][0] = 0;
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
if (frZero) {
for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {
matrix[0][i] = 0;
}
}
if (fcZero) {
for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] matrix = { {1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1} };
solution(matrix);
System.out.println();
matrix = new int[][]{ {1, 1, 0}, {1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 1} };
solution(matrix);
}
}
1 0 1
0 0 0
1 0 1
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
문제 설명
1번부터 N번까지 N개의 풍선이 원형으로 놓여 있고. i번 풍선의 오른쪽에는 i+1번 풍선이 있고, 왼쪽에는 i-1번 풍선이 있다.
단, 1번 풍선의 왼쪽에 N번 풍선이 있고, N번 풍선의 오른쪽에 1번 풍선이 있다.
각 풍선 안에는 종이가 하나 들어있고, 종이에는 -N보다 크거나 같고, N보다 작거나 같은 정수가 하나 적혀있다.
이 풍선들을 다음과 같은 규칙으로 터뜨린다.
우선, 제일 처음에는 1번 풍선을 터뜨린다.
다음에는 풍선 안에 있는 종이를 꺼내어 그 종이에 적혀있는 값만큼 이동하여 다음 풍선을 터뜨린다.
양수가 적혀 있을 경우에는 오른쪽으로, 음수가 적혀 있을 때는 왼쪽으로 이동한다.
이동할 때에는 이미 터진 풍선은 빼고 이동한다.
예를 들어 다섯 개의 풍선 안에 차례로 3, 2, 1, -3, -1이 적혀 있었다고 하자.
이 경우 3이 적혀 있는 1번 풍선, -3이 적혀 있는 4번 풍선, -1이 적혀 있는 5번 풍선, 1이 적혀 있는 3번 풍선, 2가 적혀 있는 2번 풍선의 순서대로 터지게 된다.
입력 예시
| 입력 | 결과 |
|---|---|
| 3, 2, 1, -3, -1 | 1 4 5 3 2 |
| 3, 2, -1, -2 | 1 4 2 3 |
class Node {
int data;
int cmd;
boolean visited;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int data, int cmd, boolean visited, Node next, Node prev) {
this.data = data;
this.cmd = cmd;
this.visited = visited;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
class LinkedListC {
Node head;
public void add(int data, int cmd) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, cmd, false, null, null);
this.head.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = this.head;
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != this.head) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, cmd,false, cur.next, cur);
this.head.prev = cur.next;
}
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution(int[] data) {
LinkedListC linkedList = new LinkedListC();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
linkedList.add(i + 1, data[i]);
}
Node cur = linkedList.head;
int visitCnt = 0;
int cmd = 0;
while (visitCnt != data.length) {
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt != Math.abs(cmd)) {
if (cmd > 0) {
cur = cur.next;
} else {
cur = cur.prev;
}
if (cur.visited == false) {
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur.visited = true;
visitCnt++;
cmd = cur.cmd;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] balloon = {3, 2, 1, -3, -1};
solution(balloon);
System.out.println();
balloon = new int[]{3, 2, -1, -2};
solution(balloon);
}
}
1 4 5 3 2
1 4 2 3
문제 설명
입력 문자열에서 괄호 짝 검사하여 이상이 없는지 판별하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- 괄호의 종류: (), {}, []
- 괄호 짝 이상이 없으면 Pass 출력
- 괄호 짝 이상이 있으면 Fail 출력
- 괄호 짝 이상 유무는 괄호를 열었으면 그에 대응되는 괄호로 닫혀 있는 것으로 판별한다.
입출력 예시
| 입력 문자열 | 결과 |
|---|---|
| “[yyyy]-[mm]-[dd]” | Pass |
| “System.out.println(arr[0][1))” | Fail |
| “Support [Java or Python(3.x)]” | Pass |
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Practice4 {
public static void solution(String str) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack();
boolean checkFlag = true;
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap();
map.put("(", ")");
map.put("{", "}");
map.put("[", "]");
for(String s: str.split("")) {
if (map.containsKey(s)) {
stack.push(s);
} else if (map.containsValue(s)) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
checkFlag = false;
break;
} else {
String cur = stack.pop();
if (!s.equals(map.get(cur))) {
checkFlag = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (checkFlag && stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("PASS");
} else {
System.out.println("FAIL");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution("[yyyy]-[mm]-[dd]"); // Pass
solution("System.out.println(arr[0][1))"); // FAIL
solution("Support [Java or Python(3.x)]"); // PASS
solution("([[{}])"); // FAIL
}
}
PASS
FAIL
PASS
FAIL
문제 설명
‘Dummy’ 라는 도스게임이 있다. 이 게임에는 뱀이 나와서 기어다니는데, 사과를 먹으면 뱀 길이가 늘어난다. 뱀이 이리저리 기어다니다가 벽 또는 자기자신의 몸과 부딪히면 게임이 끝난다.
게임은 NxN 정사각 보드위에서 진행되고, 몇몇 칸에는 사과가 놓여져 있다. 보드의 상하좌우 끝에 벽이 있다. 게임이 시작할때 뱀은 맨위 맨좌측에 위치하고 뱀의 길이는 1 이다. 뱀은 처음에 오른쪽을 향한다.
뱀은 매 초마다 이동을 하는데 다음과 같은 규칙을 따른다.
- 먼저 뱀은 몸길이를 늘려 머리를 다음칸에 위치시킨다.
- 만약 이동한 칸에 사과가 있다면, 그 칸에 있던 사과가 없어지고 꼬리는 움직이지 않는다.
- 만약 이동한 칸에 사과가 없다면, 몸길이를 줄여서 꼬리가 위치한 칸을 비워준다. 즉, 몸길이는 변하지 않는다.
-
사과의 위치와 뱀의 이동경로가 주어질 때 이 게임이 몇 초에 끝나는지 계산하라.
- 입력
- 보드의 크기 N (2 ≤ N ≤ 100)
- 사과의 개수 K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100)
- 뱀의 방향 변환 횟수 L (1 ≤ L ≤ 100)
- 사과의 위치가 담긴 리스트 apples
- 첫 번째 정수는 행, 두 번째 정수는 열 위치를 의미한다. 사과의 위치는 모두 다르며, 맨 위 맨 좌측 (1행 1열) 에는 사과가 없다.
- 뱀의 방향 변환 정보 moves
- 정수 X와 문자 C로 이루어져 있으며. 게임 시작 시간으로부터 X초가 끝난 뒤에 왼쪽(C가 ‘L’) 또는 오른쪽(C가 ‘D’)로 90도 방향을 회전시킨다는 뜻이다. X는 10,000 이하의 양의 정수이며, 방향 전환 정보는 X가 증가하는 순으로 주어진다.
입출력 예시
- 예시입력1
- 입력
N = 6 K = 3 L = 3 apples = [(3, 4), (2, 5), (5, 3)] moves = [(3, 'D'), (15, 'L'), (17, 'D')] - 출력: 9
- 입력
- 예시입력2
- 입력
N = 10 K = 4 L = 4 apples = [(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5)] moves = [(8, 'D'), (10, 'D'), (11, 'D'), (13, 'L')] - 출력: 21
- 입력
- 예시입력3
- 입력
N = 10 K = 5 L = 4 apples = [(1, 5), (1, 3), (1, 2), (1, 6), (1, 7)] moves = [(8, 'D'), (10, 'D'), (11, 'D'), (13, 'L')] - 출력: 13
- 입력
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Practice5 {
public static Integer solution(int n, int k, int l, ArrayList<ArrayList> apples, Queue<ArrayList> moves) {
int[][] board = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for (ArrayList item: apples) {
board[(int)item.get(0)][(int)item.get(1)] = 1;
}
Queue<ArrayList> snake = new LinkedList();
snake.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 1)));
ArrayList<ArrayList> direction = new ArrayList();
direction.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(0, 1)));
direction.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 0)));
direction.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(0, -1)));
direction.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(-1, 0)));
int dIdx = 0;
int score = 0;
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
while (true) {
score += 1;
x += (int)direction.get(dIdx).get(0);
y += (int)direction.get(dIdx).get(1);
if (1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= n) {
ArrayList cur = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(x, y));
if (snake.contains(cur)) {
return score;
}
snake.add(cur);
if (board[x][y] == 0) {
snake.poll();
} else if (board[x][y] == 1) {
board[x][y] = 0;
}
} else {
return score;
}
if (moves.size() > 0 && score == (int)moves.peek().get(0)) {
if ((char)moves.peek().get(1) == 'D') {
dIdx = (dIdx + 1) % 4;
moves.poll();
} else if ((char)moves.peek().get(1) == 'L') {
dIdx = (dIdx - 1) % 4;
moves.poll();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int n = 6;
int k = 3;
int l = 3;
ArrayList<ArrayList> apples = new ArrayList();
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(3, 4)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(2, 5)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(5, 3)));
Queue<ArrayList> moves = new LinkedList();
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(3, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(15, 'L')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(7, 'D')));
System.out.println((solution(n, k, l, apples, moves)));
n = 10;
k = 4;
l = 4;
apples.clear();
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 3)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 4)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 5)));
moves.clear();
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(8, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(10, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(11, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(13, 'L')));
System.out.println((solution(n, k, l, apples, moves)));
n = 10;
k = 5;
l = 4;
apples.clear();
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 5)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 3)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 6)));
apples.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 7)));
moves.clear();
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(8, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(10, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(11, 'D')));
moves.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(13, 'L')));
System.out.println((solution(n, k, l, apples, moves)));
}
}
9
21
13

Leave a comment