스택
스택 (Stack)
후입선출 (Last In First Out; LIFO) 자료구조
마지막에 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 구조
데이터가 입력된 순서의 역순으로 처리되어야 할 때 사용
ex) 함수 콜 스택, 수식 계산, 인터럽트 처리 등
스택 기본 구조
후입 선출 구조
기본적으로 데이터 추가, 꺼내기, 스택 공간 확인 동작으로 이루어짐
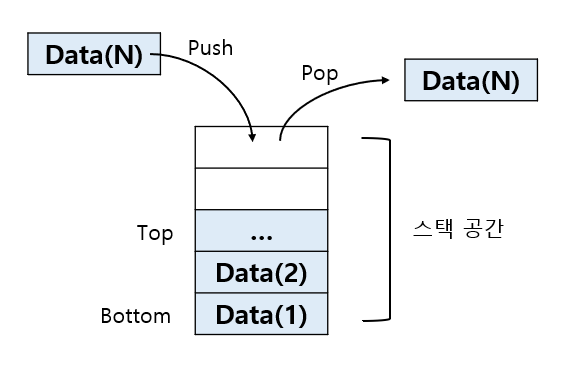
스택 기본 연산
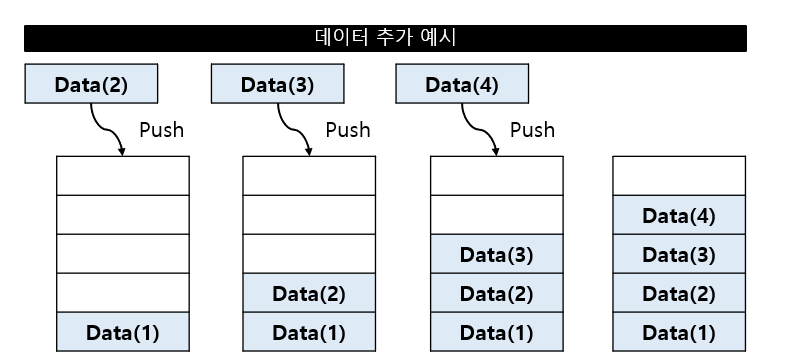
데이터 추가 (Push)
스택의 가장 마지막 위치에 데이터 추가
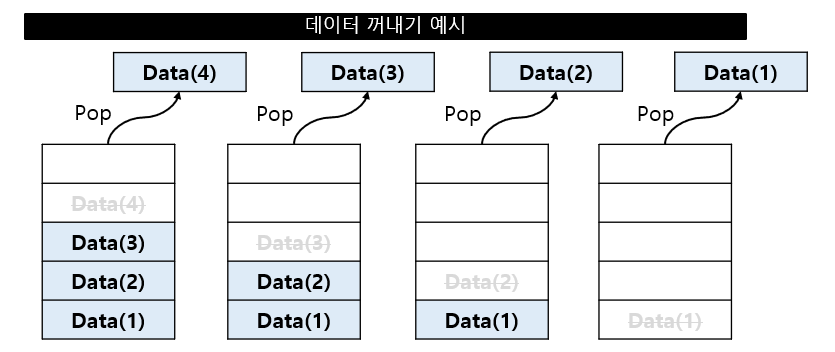
데이터 꺼내기 (Pop)
스택의 가장 마지막 위치에서 데이터 꺼냄
선형 자료구조 - 스택
스택 구현
// 선형 자료구조 - 스택
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.contains(1));
System.out.println(stack.size());
System.out.println(stack.empty());
stack.clear();
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
5
[1, 2, 3, 4]
4
[1, 2, 3]
3
[1, 2, 3]
true
3
false
[]
Exception in thread "main" java.util.EmptyStackException
at java.base/java.util.Stack.peek(Stack.java:101)
at java.base/java.util.Stack.pop(Stack.java:83)
at Main.main(Main.java:31)
ArrayList 를 이용한 스택 구현
// Practice1
// ArrayList 를 이용한 스택 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MyStack1 {
ArrayList list;
MyStack1() {
this.list = new ArrayList();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.list.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public void push(int data) {
this.list.add(data);
}
public Integer pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty!");
return null;
}
int data = (int)this.list.get(this.list.size() - 1);
this.list.remove(this.list.size() - 1);
return data;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty!");
return null;
}
int data = (int)this.list.get(this.list.size() - 1);
return data;
}
public void printStack() {
System.out.println(this.list);
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyStack1 myStack = new MyStack1();
myStack.isEmpty();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(3);
myStack.push(4);
myStack.push(5);
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myStack.peek()); // 5
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 5
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 4
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 3
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 2
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 1
myStack.printStack();
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
5
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
5
4
[1, 2, 3]
3
2
1
[]
배열을 이용한 기본 스택 직접 구현
// Practice2
// 배열을 이용한 기본 스택 직접 구현
class MyStack2 {
int[] arr;
int top = -1;
MyStack2(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.top == -1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean isFull() {
if (this.top == this.arr.length - 1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public void push(int data) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("Stack is full!");
return;
}
this.top += 1;
this.arr[this.top] = data;
}
public Integer pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty!");
return null;
}
int data = this.arr[this.top];
this.top -= 1;
return data;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty!");
return null;
}
return this.arr[this.top];
}
public void printStack() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.top + 1; i++) {
System.out.print(this.arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyStack2 myStack = new MyStack2(5);
myStack.isEmpty();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(3);
myStack.push(4);
myStack.push(5);
myStack.push(6);
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myStack.peek()); // 5
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 5
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 4
myStack.printStack(); // 1, 2, 3
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 3
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 2
System.out.println(myStack.pop()); // 1
myStack.printStack();
}
}
Stack is full!
1 2 3 4 5
5
1 2 3 4 5
5
4
1 2 3
3
2
1
문제풀이
// Practice1
// 문자열 뒤집기
// 입출력 예시)
// 입력: "Hello"
// 출력: "OlleH"
// 입력: 1 3 5 7 9
// 출력: 9 7 5 3 1
import java.util.Stack;
public class Practice1 {
public static String reverseString(String str) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
String result = "";
for(String s: str.split("")) {
stack.push(s);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result = result + stack.pop();
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String result = reverseString("Hello");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
result = reverseString("1 3 5 7 9");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}
result = olleH
result = 9 7 5 3 1
// Practice2
// 괄호 짝 검사
// 입출력 예시)
// 입력: "("
// 출력: Fail
// 입력: ")"
// 출력: Fail
// 입력: "()"
// 출력: Pass
import java.util.Stack;
public class Practice2 {
public static void checkParenthesis(String str) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
boolean checkFlag = true;
for(String s: str.split("")) {
if (s.equals("(")) {
stack.push(s);
} else {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
checkFlag = false;
break;
} else {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
if (checkFlag && stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("PASS!");
} else {
System.out.println("FAIL!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
checkParenthesis("("); // FAIL!
checkParenthesis(")"); // FAIL!
checkParenthesis("()"); // PASS!
checkParenthesis("()()()"); // PASS!
checkParenthesis("(())()"); // PASS!
checkParenthesis("(((()))"); // FAIL!
}
}
FAIL!
FAIL!
PASS!
PASS!
PASS!
FAIL!
// Practice3
// 후위표기법 연산
// 참고 설명) 전위/중위/후위 표기법
// 입출력 예시)
// 입력: "2 2 +"
// 출력: 4
// 입력: "2 2 -"
// 출력: 0
import java.util.Stack;
public class Practice3 {
public static double calculate(String string) {
Stack<Double> stack = new Stack<Double>();
for (String str: string.split(" ")) {
if (str.equals("+")) {
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
} else if (str.equals("-")) {
stack.push(- stack.pop() + stack.pop());
} else if (str.equals("*")) {
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
} else if (str.equals("/")) {
stack.push(1 / stack.pop() * stack.pop());
} else {
stack.push(Double.parseDouble(str));
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(calculate("2 2 +")); // 4
System.out.println(calculate("2 2 -")); // 0
System.out.println(calculate("2 2 *")); // 4
System.out.println(calculate("2 2 /")); // 1
System.out.println(calculate("1 1 + 2 * 3 * 2 / 5 -")); // 1
System.out.println(calculate("5 2 * 3 - 8 * 4 /")); // 14
}
}
4.0
0.0
4.0
1.0
1.0
14.0
// Practice4
// 두 문자열 비교
// 단, #은 backspace 로 바로 이전의 문자를 삭제하는 기능이라고 가정
// 입출력 예시
// 입력: s1 = "tree", s2 = "th#ree"
// 출력: true
// 입력: s1 = "ab#a", s2 = "aab#"
// 출력: true
// 입력: s1 = "wo#w", s2 = "ww#o"
// 출력: false
import java.util.Stack;
public class Practice4 {
public static boolean stringCompare(String s1, String s2) {
String s1After = doBackspace(s1);
String s2After = doBackspace(s2);
return s1After.equals(s2After);
}
public static String doBackspace(String s) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
for (char c: s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '#' && !stack.empty()) {
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(c);
}
}
return String.valueOf(stack);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String s1 = "tree";
String s2 = "th#ree";
System.out.println(stringCompare(s1, s2));
s1 = "ab#a";
s2 = "aab#";
System.out.println(stringCompare(s1, s2));
s1 = "wo#w";
s2 = "ww#o";
System.out.println(stringCompare(s1, s2));
}
}
true
true
false
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment