연결 리스트
연결 리스트 (Linked List)
데이터를 링크로 연결해서 관리하는 자료구조
자료의 순서는 정해져 있지만,
메모리상 연속성이 보장되지는 않음
연결 리스트의 장점
데이터 공간을 미리 할당할 필요 없음
즉, 리스트의 길이가 가변적이라 데이터 추가/삭제 용이
연결 리스트의 단점
연결구조를 위한 별도 데이터 공간 필요
연결 정보를 찾는 시간이 필요 (접근 속도가 상대적으로 느림)
데이터 추가, 삭제 시 앞뒤 데이터의 연결을 재구성하는 작업 필요
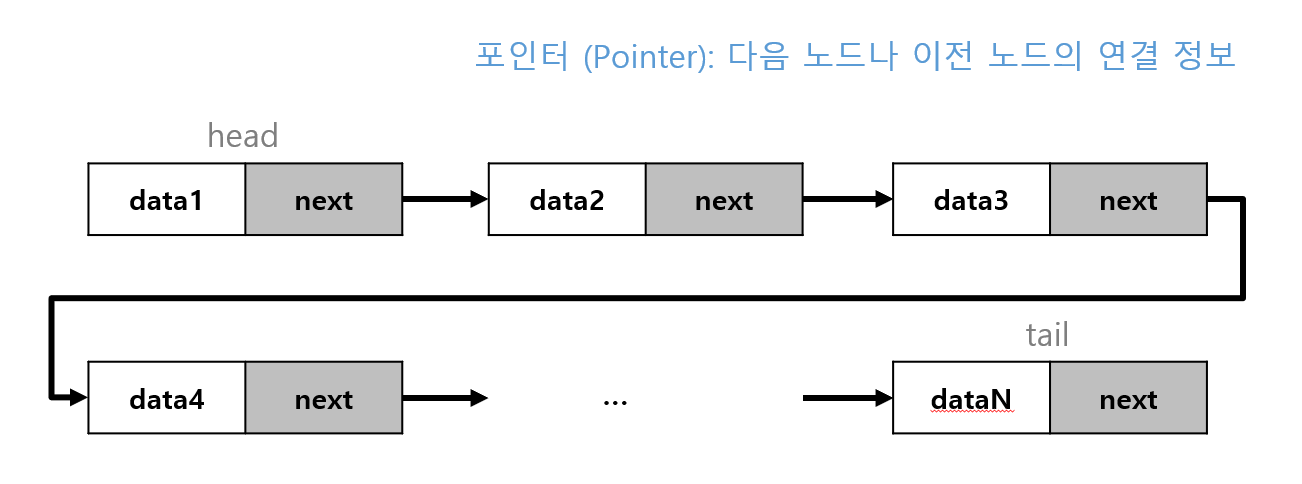
연결 리스트 기본 구조
노드 (Node)
데이터 저장 단위로, 값과 포인터로 구성
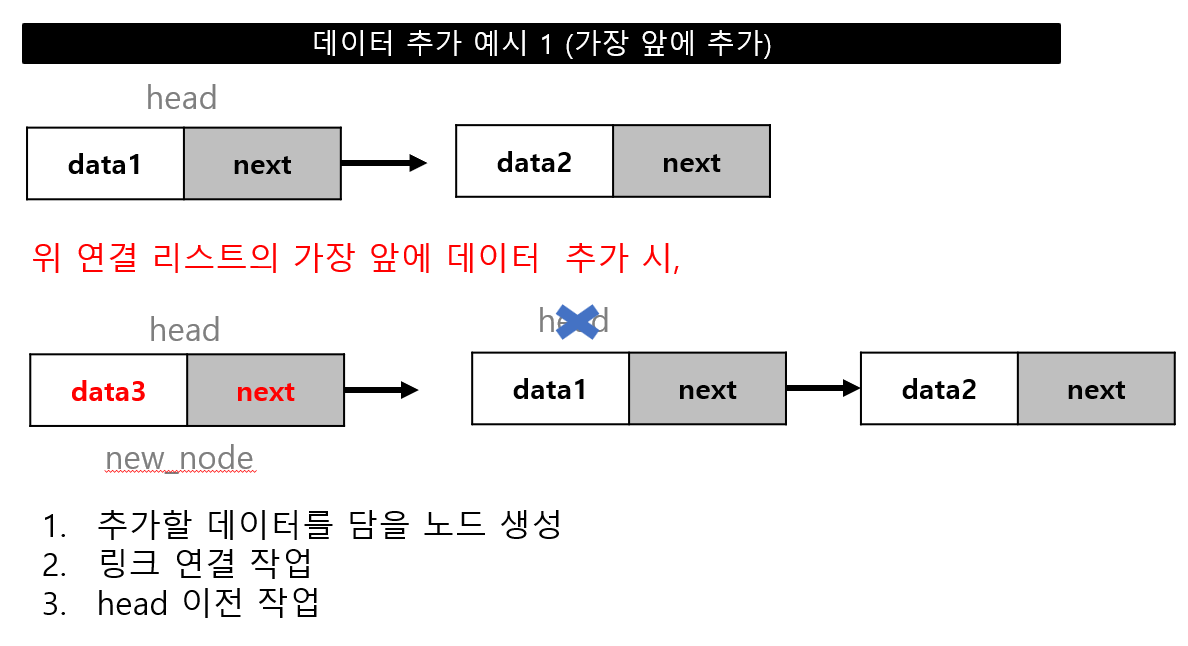
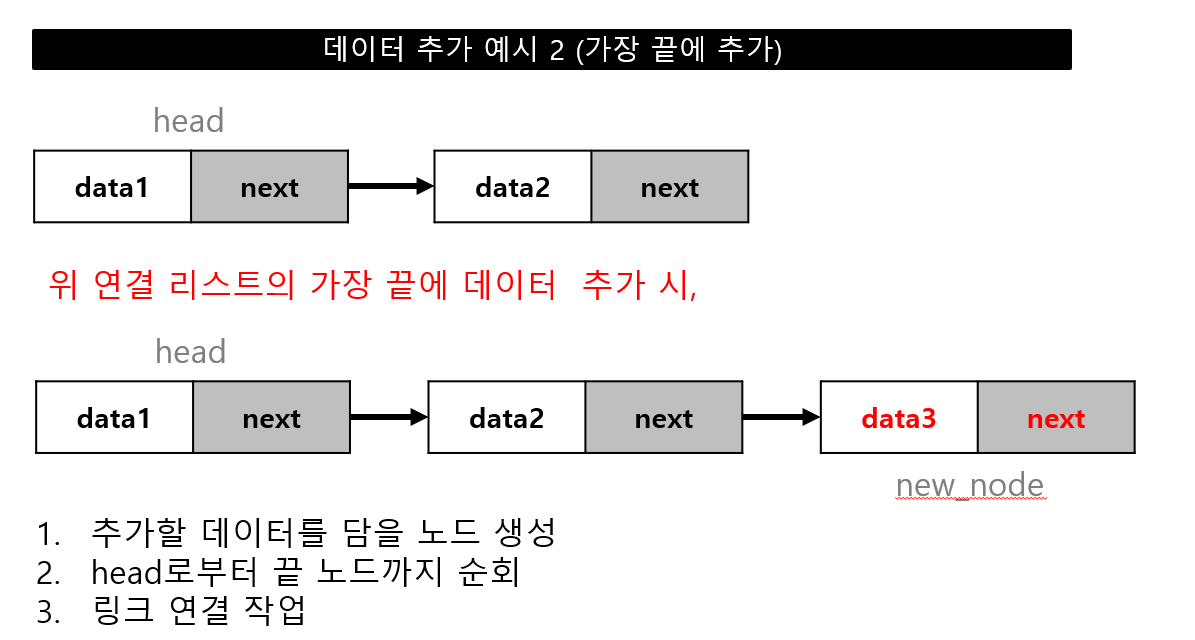
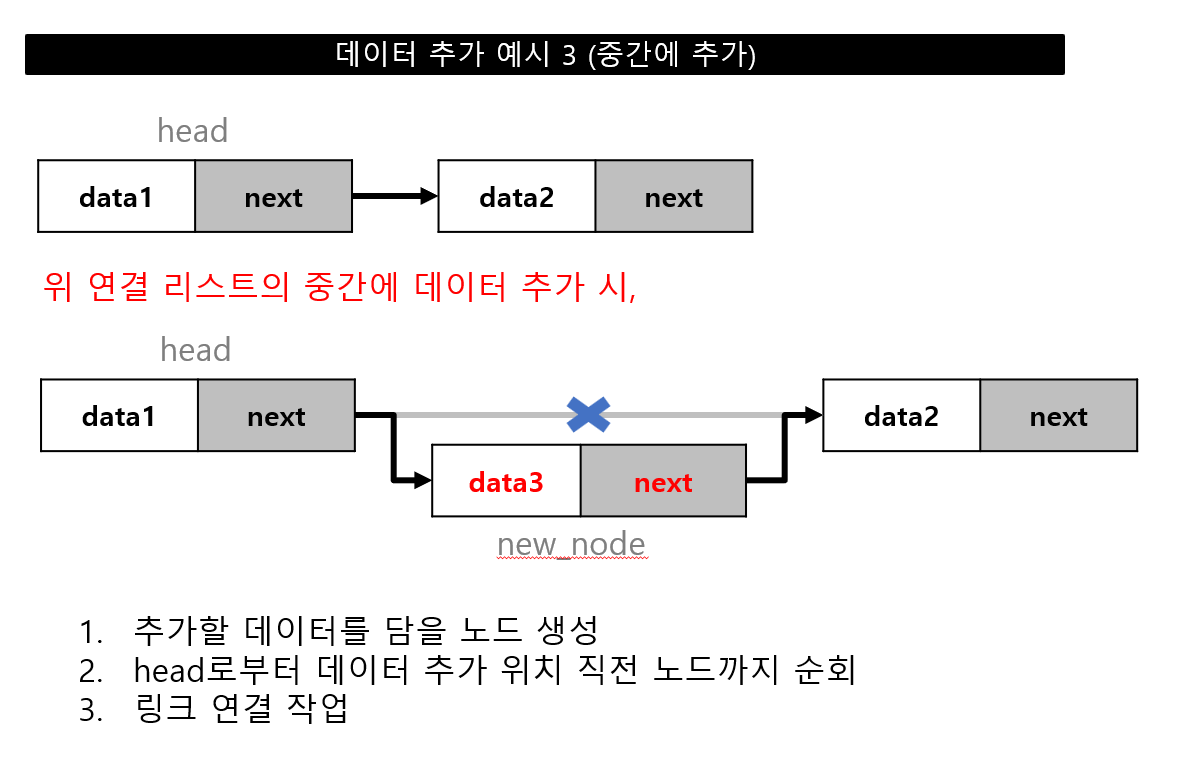
데이터 추가
데이터 추가 위치(head, 중간, tail)에 따른 연결 작업 필요
데이터 삭제
데이터 삭제 위치(head, 중간, tail)에 따른 연결 작업 필요
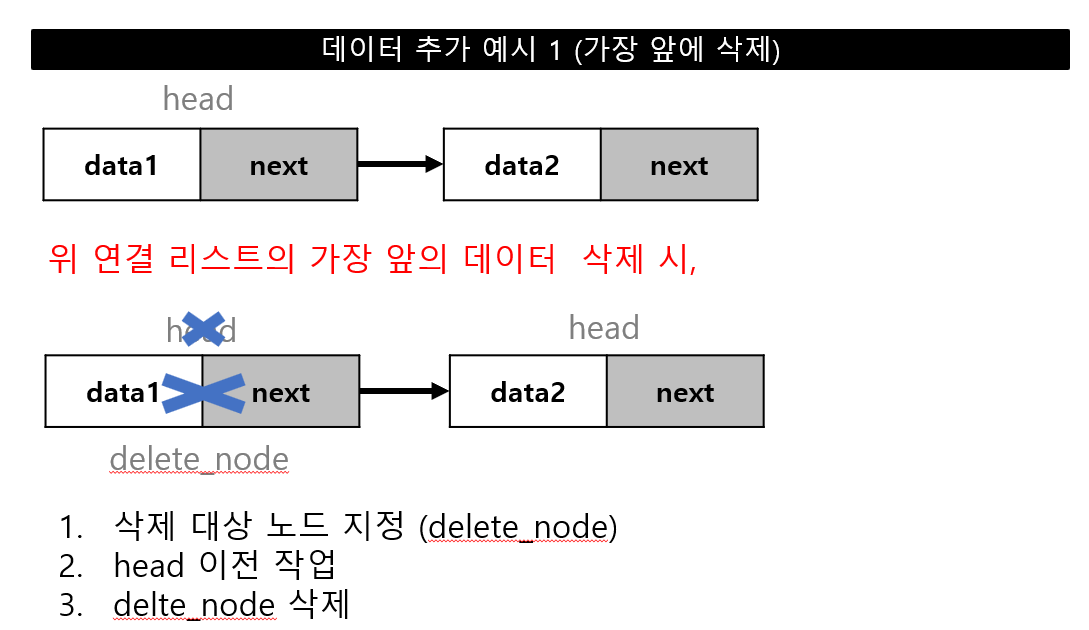
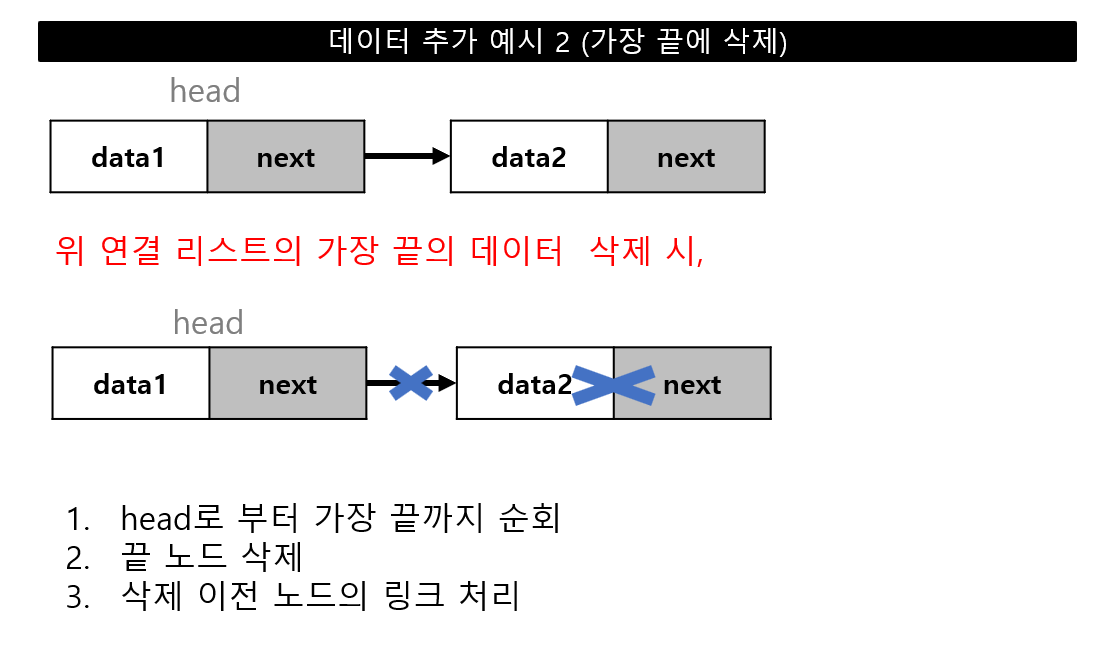
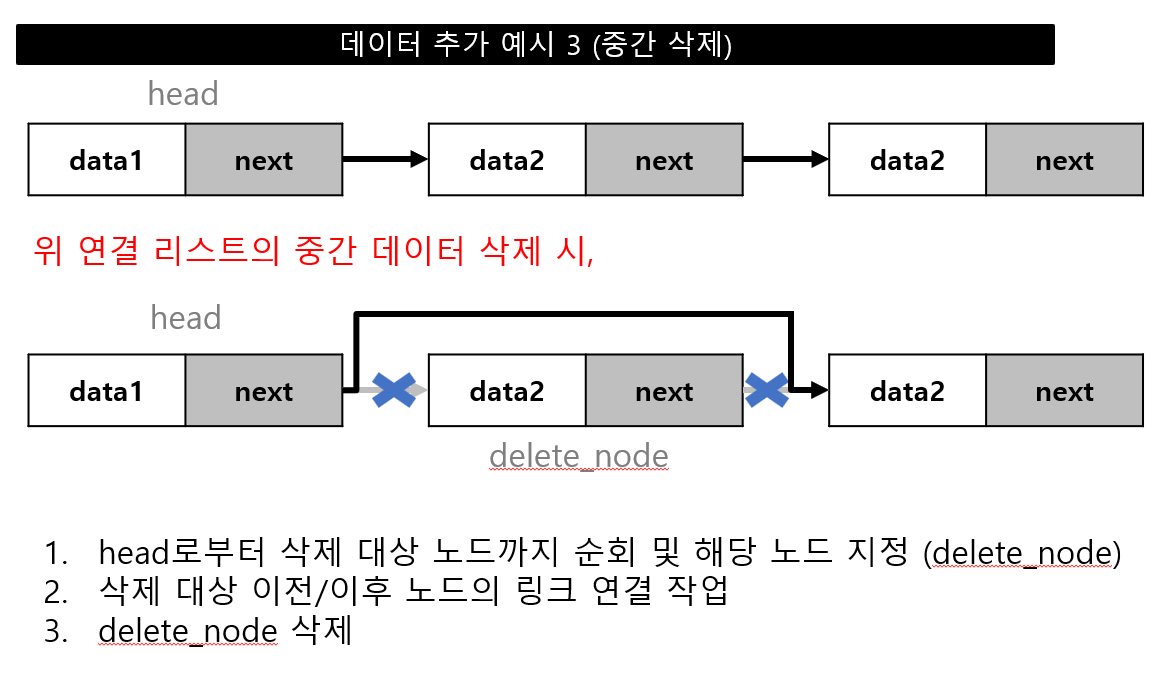
선형 자료구조 - 연결 리스트
단순 연결 리스트 기본 구조 구현
// 선형 자료구조 - 연결 리스트
// 단순 연결 리스트 (simple ver.) 기본 구조 구현
// 노드
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
// 연결 리스트 비어있는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 연결 리스트의 맨 뒤에 데이터 추가
public void addData(int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
// 연결 리스트의 맨 뒤의 데이터 삭제
public void removeData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node prev = cur;
while (cur.next != null) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = null;
} else {
prev.next = null;
}
}
// 연결 리스트에서 데이터 찾기
public void findData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
}
// 연결 리스트의 모든 데이터 출력
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test Code
LinkedList myList = new LinkedList(new Node(1, null));
myList.showData(); // 1
myList.addData(2);
myList.addData(3);
myList.addData(4);
myList.addData(5);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.findData(3); // Data exist!
myList.findData(100); // Data not found!
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.showData(); // 1 2
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData();
myList.removeData(); // List is empty
}
}
1
1 2 3 4 5
Data exist!
Data not found!
1 2
List is empty
단순 연결 리스트 구현 완성
// Practice1
// 단순 연결 리스트 구현 완성
class LinkedList2 extends LinkedList {
LinkedList2(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
// 연결 리스트에 데이터 추가
// before_data 가 null 인 경우, 가장 뒤에 추가
// before_data 에 값이 있는 경우, 해당 값을 가진 노드 앞에 추가
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else if (beforeData == null) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
} else {
pre.next = new Node(data, cur);
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
// 연결 리스트에서 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
LinkedList2 myList = new LinkedList2(new Node(1, null));
myList.showData(); // 1
myList.addData(2);
myList.addData(3);
myList.addData(4);
myList.addData(5);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData(); // 100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData(); // List is empty!
}
}
1
1 2 3 4 5
100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
1 2 3 4 5
List is empty!
양방향 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List) 구현
// Practice2
// 양방향 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List) 구현
class NodeBi {
int data;
NodeBi next;
NodeBi prev;
NodeBi(int data, NodeBi next, NodeBi prev) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
NodeBi head;
NodeBi tail;
DoublyLinkedList(NodeBi node) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
// 연결 리스트 비어있는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 연결 리스트에 데이터 추가
// before_data 가 null 인 경우, 가장 뒤에 추가
// before_data 에 값이 있는 경우, 해당 값을 가진 노드 앞에 추가
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new NodeBi(data, null, null);
this.tail = this.head;
} else if (beforeData == null) {
this.tail.next = new NodeBi(data, null, this.tail);
this.tail = this.tail.next;
} else {
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = new NodeBi(data, this.head, null);
this.head.next.prev = this.head;
} else {
pre.next = new NodeBi(data, cur, pre);
cur.prev = pre.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
// 연결 리스트에서 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head && cur == this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
this.head.prev = null;
} else if (cur == this.tail) {
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = pre;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 연결 리스트의 모든 데이터 출력
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 연결 리스트의 모든 데이터 출력 (tail 부터)
public void showDataFromTail() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
DoublyLinkedList myList = new DoublyLinkedList(new NodeBi(1, null, null));
myList.showData(); // 1
myList.addData(2, null);
myList.addData(3, null);
myList.addData(4, null);
myList.addData(5, null);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.showDataFromTail(); // 5 4 3 2 1
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData(); // 100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
myList.showDataFromTail(); // 5 500 4 400 3 300 2 200 1 100
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.showDataFromTail(); // 5 4 3 2 1
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData(); // List is empty!
myList.showDataFromTail(); // List is empty!
}
}
1
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 3 2 1
100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
5 500 4 400 3 300 2 200 1 100
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 3 2 1
List is empty!
List is empty
원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List) 구현
// Practice3
// 원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List) 구현
class CircularLinkedList {
NodeBi head;
NodeBi tail;
CircularLinkedList(NodeBi node) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
node.next = this.head;
node.prev = this.head;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 연결 리스트에 데이터 추가
// before_data 가 null 인 경우, 가장 뒤에 추가
// before_data 에 값이 있는 경우, 해당 값을 가진 노드 앞에 추가
public void addData(int data, Integer beforeData) {
if (this.head == null) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, null, null);
this.head = newNodeBi;
this.tail = newNodeBi;
newNodeBi.next = newNodeBi;
newNodeBi.prev = newNodeBi;
} else if (beforeData == null) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, this.head, this.tail);
this.tail.next= newNodeBi;
this.head.prev = newNodeBi;
this.tail = newNodeBi;
} else {
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
do {
if (cur.data == beforeData) {
if (cur == this.head) {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, this.head, this.tail);
this.tail.next = newNodeBi;
this.head.prev = newNodeBi;
this.head = newNodeBi;
} else {
NodeBi newNodeBi = new NodeBi(data, cur, pre);
pre.next = newNodeBi;
cur.prev = newNodeBi;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
} while (cur != this.head);
}
}
// 연결 리스트에서 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
NodeBi pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head && cur == this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else if (cur == this.head) {
cur.next.prev = this.head.prev;
this.head = cur.next;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else if (cur == this.tail) {
pre.next = this.tail.next;
this.tail = pre;
this.head.prev = this.tail;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = pre;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
NodeBi cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(cur.data);
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
CircularLinkedList myList = new CircularLinkedList(new NodeBi(1, null, null));
myList.addData(2, null);
myList.addData(3, null);
myList.addData(4, null);
myList.addData(5, null);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.addData(100, 1);
myList.addData(200, 2);
myList.addData(300, 3);
myList.addData(400, 4);
myList.addData(500, 5);
myList.showData(); // 100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
myList.removeData(300);
myList.removeData(100);
myList.removeData(500);
myList.removeData(200);
myList.removeData(400);
myList.showData(); // 1 2 3 4 5
myList.removeData(3);
myList.removeData(1);
myList.removeData(5);
myList.removeData(2);
myList.removeData(4);
myList.showData(); // List is empty!
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
100 1 200 2 300 3 400 4 500 5
1 2 3 4 5
List is empty!
문제풀이
// Practice1
// 단방향 연결 리스트에서 중복 데이터를 찾아 삭제하세요.
// 입출력 예시)
// 입력 연결 리스트: 1, 3, 3, 1, 4, 2, 4, 2
// 결과 연결 리스트: 1, 3, 4, 2
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == null;
}
public void addData(int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public boolean findData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// System.out.println("List is empty");
return false;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
// System.out.println("Data exist!");
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// System.out.println("Data not found!");
return false;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static LinkedList removeDup(LinkedList listBefore) {
LinkedList listAfter = new LinkedList();
Node cur = listBefore.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (listAfter.findData(cur.data) == false) {
listAfter.addData(cur.data);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return listAfter;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.showData(); // 1 3 3 1 4 2 4 2
linkedList = removeDup(linkedList);
linkedList.showData(); // 1 3 4 2
}
}
1 3 3 1 4 2 4 2
1 3 4 2
// Practice2
// Palindrome 연결 리스트
// 추가 자료구조 없이 연결 리스트만으로 풀어보기
// Palindrome: 앞으로 읽어도 뒤로 읽어도 같은 문자열
// 입력 예시)
// 입력 연결 리스트: 1, 3, 5, 3, 1
// 결과: true
// 입력 연결 리스트: 3, 5, 5, 3
// 결과: true
// 입력 연결 리스트: 1, 3, 5, 1
// 결과: false
public class Practice2 {
public static boolean checkPalindrome(LinkedList list) {
Node cur = list.head;
Node left = list.head;
Node right = null;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
right = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
Node prevRight = right;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt / 2; i++) {
if (left.data != right.data) {
return false;
}
left = left.next;
right = left;
while (right.next != prevRight) {
right = right.next;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(5);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(1);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList));
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList();
linkedList2.addData(3);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(3);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList2));
LinkedList linkedList3 = new LinkedList();
linkedList3.addData(1);
linkedList3.addData(3);
linkedList3.addData(5);
linkedList3.addData(1);
System.out.println(checkPalindrome(linkedList3));
}
}
true
true
false
// Practice3
// 연결 리스트 부분 뒤집기
// 주어진 연결 리스트에서 시작 위치부터 끝 위치 사이의 노드들을 뒤집으시오.
// 입력 예시)
// 입력 연결 리스트: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
// 시작 위치: 2
// 끝 위치: 4
// (처음 위치는 1부터라고 가정)
// 결과 연결 리스트: 1, 4, 3, 2, 5
public class Practice3 {
public static LinkedList reverseList(LinkedList list, int left, int right) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node pre1 = null;
cur1 = list.head;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre1 = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
Node cur2 = cur1;
Node pre2 = pre1;
Node after = null;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
after = cur2.next;
cur2.next = pre2;
pre2 = cur2;
cur2 = after;
}
pre1.next = pre2;
cur1.next = cur2;
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addData(1);
linkedList.addData(2);
linkedList.addData(3);
linkedList.addData(4);
linkedList.addData(5);
linkedList.showData();
linkedList = reverseList(linkedList, 2, 4);
linkedList.showData();
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList();
linkedList2.addData(1);
linkedList2.addData(2);
linkedList2.addData(3);
linkedList2.addData(4);
linkedList2.addData(5);
linkedList2.addData(6);
linkedList2.addData(7);
linkedList2.showData();
linkedList2 = reverseList(linkedList2, 3, 5);
linkedList2.showData();
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
1 4 3 2 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 5 4 3 6 7
package P4;
// Practice4
// 연결 리스트 배열 사용 연습
// 주어진 문자열 배열을 연결 리스트 배열로 관리하는 코드를 작성하시오.
// 관리 규칙은 다음과 같다.
// 각 문자열의 첫 글자가 같은 것끼리 같은 연결 리스트로 관리하기
import java.util.HashSet;
class Node {
String data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(String data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
char alphabet;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node, char alphabet) {
this.head = node;
this.alphabet = alphabet;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == null;
}
public void addData(String data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(data, null);
}
}
public void removeData(String data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data.equals(data)) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public boolean findData(String data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return false;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data.equals(data)) {
System.out.println("Data exist!");
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
return false;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice4 {
public static void dataCollect(String[] data) {
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet();
for (String item: data) {
set.add(item.toCharArray()[0]);
}
System.out.println(set);
Character[] arr = set.toArray(new Character[0]);
LinkedList[] linkedList = new LinkedList[set.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.length; i++) {
linkedList[i] = new LinkedList(null, arr[i]);
}
for (String item: data) {
for (LinkedList list: linkedList) {
if (list.alphabet == item.toCharArray()[0]) {
list.addData(item);
}
}
}
for (LinkedList list: linkedList) {
System.out.print(list.alphabet + ": ");
list.showData();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
String[] input = {"apple", "watermelon", "banana", "apricot", "kiwi", "blueberry", "cherry", "orange"};
dataCollect(input);
System.out.println();
String[] input2 = {"ant", "kangaroo", "dog", "cat", "alligator", "duck", "crab", "kitten", "anaconda", "chicken"};
dataCollect(input2);
}
}
[a, b, c, w, k, o]
a: apple apricot
b: banana blueberry
c: cherry
w: watermelon
k: kiwi
o: orange
[a, c, d, k]
a: ant alligator anaconda
c: cat crab chicken
d: dog duck
k: kangaroo kitten
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment