연습문제풀이-3
Practice1
문제 설명
정수형 오름차순 데이터가 nums 라는 배열에 주어졌다.
현재 배열 내에는 중복된 데이터들이 들어있을 수 있는데 해당 중복들을 제거하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
이 때, 추가 배열을 사용하지 않고 중복 데이터들을 제거해야 하며
nums 배열 하나 만 사용하여 중복 데이터를 제거 후
정렬된 데이터를 출력하세요.
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 1, 1, 2 | 1, 2 |
| 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4 | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 |
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(int[] nums) {
int idx = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
// 정렬되어 있는 배열이므로 idx 가 0일 때와, 이전 값보다 클 때만 nums 에 업데이트
if (idx == 0 || num > nums[idx - 1]) {
nums[idx++] = num;
}
}
System.out.print("[" + idx + "] ");
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution(new int[] {1, 1, 2});
solution(new int[] {0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4});
}
}
[2] 1 2
[5] 0 1 2 3 4
Practice2
문제 설명
주어진 nums 배열에서 두 번 나타나는 모든 정수의 배열을 반환하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- nums 배열은 [1, n] 범위의 정수로 이루어져 있다.
- 각 정수는 한 번 또는 두 번 나타날 수 있다.
반환을 위한 메모리 공간 외에 추가 적인 배열 사용은 하지 않는다.
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 4, 3, 2, 7, 8, 2, 3, 1 | 2, 3 |
| 1, 1, 2 | 1 |
| 1, 3, 1, 3, 5, 5 | 1, 3, 5 |
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice2 {
public static ArrayList<Integer> solution(int[] nums) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// [1, n]의 범위로 이루어져 있는 것과 최대 2번 까지 나타날 수 있는 것을 이용
// 각 원소의 값을 인덱스 삼아 해당 위치의 값에 부호처리를 하면
// 같은 값이 있는지 여부를 체크할 수 있음
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int index = Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1;
if (nums[index] < 0) {
list.add(Math.abs(index + 1));
}
nums[index] = -nums[index];
}
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {4, 3, 2, 7, 8, 2, 3, 1};
System.out.println(solution(nums));
nums = new int[]{1, 1, 2};
System.out.println(solution(nums));
nums = new int[]{1, 3, 1, 3, 5, 5};
System.out.println(solution(nums));
}
}
[2, 3]
[1]
[1, 3, 5]
Practice3
문제 설명
정렬된 정수형 배열 arr 이 주어졌을 때, 다음을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
- arr 과 함께 k 와 x 가 주어진다.
- k 는 개수, x 는 기준 값이다.
- x 와 절대 값 차이 기준으로 가까운 수를 k 개수 만큼 정렬된 순서로 출력하세요.
- 절대 값 차이가 같을 때는 숫자가 작은 것이 먼저 출력되도록 한다.
| 입력 | k | x | 출력 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 4 | 3 | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 | 5 | 5 | 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
| 2, 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 2, 4 | 3 | 3 | 2, 4 |
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution(int[] arr, int k, int x) {
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
// 해시 맵에 차이 값을 키로, 해당 숫자들은 값으로 리스트 형태로 뒤로 이어줌
// 이 때, 작은 숫자들이 앞쪽에 오도록 정렬하여 추가
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int diff = Math.abs(x - arr[i]);
ArrayList<Integer> cur = map.get(diff);
if (cur == null) {
map.put(diff, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(arr[i])));
} else {
int idx = cur.size();
for (int j = 0; j < cur.size(); j++) {
if (cur.get(j) > arr[i]) {
idx = j;
break;
}
}
cur.add(idx, arr[i]);
}
}
// 해시 맵에서 작은 diff 순으로 꺼내서 k 개 만큼 결과 쌓일 때 까지 반복
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int cnt = 0;
while (map.size() > 0) {
// 최소 값 구하기 예시
int minDiff = map.keySet().stream().min((a, b) -> a - b).get();
ArrayList<Integer> cur = map.get(minDiff);
map.remove(minDiff); // 꺼낸 후에는 map 에서 삭제
while (cur.size() > 0) { // k 개 만큼 출력하기 전에 데이터가 소진될 수도 있음
result.add(cur.get(0));
cur.remove(0); // 꺼낸 숫자는 리스트에서 삭제
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) {
break;
}
}
if (cnt == k) {
break;
}
}
Collections.sort(result); // 정렬 예시
System.out.println(result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
solution(arr, 4, 3);
arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
solution(arr, 5, 5);
arr = new int[]{2, 4};
solution(arr, 1, 3);
arr = new int[]{2, 4};
solution(arr, 3, 3);
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
[2]
[2, 4]
Practice4
문제 설명
MxN 행렬 정보가 2차원 정수형 배열 matrix 에 주어지면
아래 그림과 같이 나선형 모양으로 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
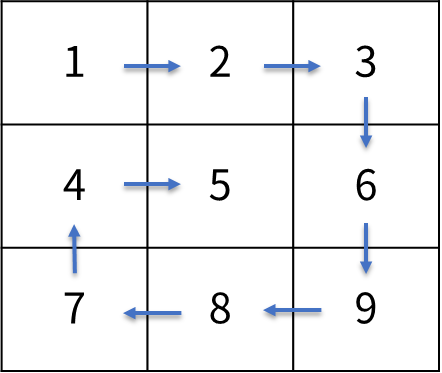
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} } | 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 5 |
| { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10 ,11 ,12} } | 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 11, 10, 9, 5, 6, 7 |
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice4 {
public static ArrayList<Integer> solution(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int rowStart = 0;
int rowEnd = matrix.length - 1;
int colStart = 0;
int colEnd = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (rowStart <= rowEnd && colStart <= colEnd) {
// 오른쪽 방향 이동
for (int i = colStart; i <= colEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[rowStart][i]);
}
rowStart++;
// 아래쪽 방향 이동
for (int i = rowStart; i <= rowEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][colEnd]);
}
colEnd--;
// 왼쪽 방향 이동
if (rowStart <= rowEnd) {
for (int i = colEnd; i >= colStart; i--) {
result.add(matrix[rowEnd][i]);
}
}
rowEnd--;
// 위쪽 방향 이동
if (colStart <= colEnd) {
for (int i = rowEnd; i >= rowStart; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][colStart]);
}
}
colStart ++;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] matrix = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} };
System.out.println((solution(matrix)));
matrix = new int[][]{ {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10 ,11 ,12} };
System.out.println((solution(matrix)));
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 11, 10, 9, 5, 6, 7]
Practice5
문제 설명
n개의 정수형 데이터가 height 배열에 주어졌다.
height 배열의 각각의 원소는 아래 그림과 같이 각 벽에 대한 높이를 의미한다.
이와 같이 높이 값들이 주어졌을 때,
벽 사이사이의 빈 공간에 담을 수 있는 물의 총량을 출력하세요.
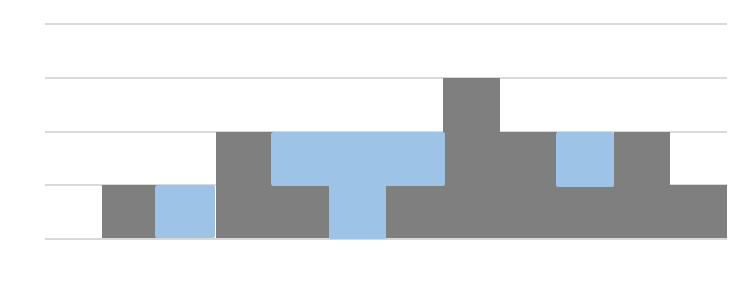
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
| 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 | 6 |
| 4, 2, 0, 3, 2, 5 | 9 |
public class Practice5 {
public static int solution(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 좌, 우 인덱스 설정
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int leftMax = 0;
int rightMax = 0;
int result = 0;
while (left < right) {
if (height[left] < height[right]) { // 왼쪽 벽이 낮은 경우
if (height[left] >= leftMax) { // 이전의 왼쪽 최대 높이 벽보다 더 큰 경우,
leftMax = height[left]; // 물이 담기진 않고 벽 높이 갱신
} else {
result += leftMax - height[left]; // 그 외의 경우는 높이 줄어든 만큼 물이 담김
}
left++;
} else { // 오른쪽 벽이 낮은 경우
if (height[right] >= rightMax) {
rightMax = height[right];
} else {
result += rightMax - height[right];
}
right--;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] height = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
System.out.println(solution(height));
height = new int[]{4, 2, 0, 3, 2, 5};
System.out.println(solution(height));
}
}
6
9

Leave a comment