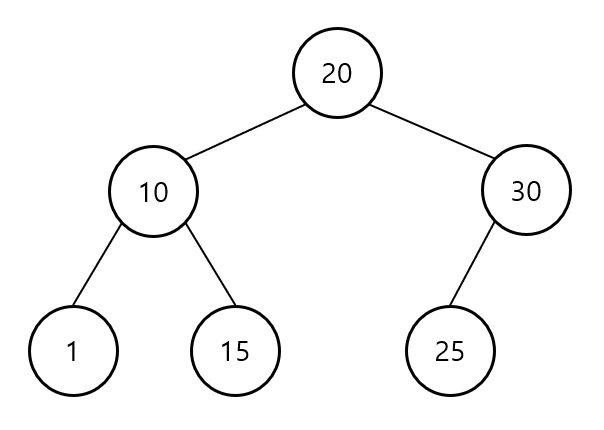
이진 탐색트리
이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree)
아래의 규칙으로 구성된 이진 트리
왼쪽 자식 노드의 키는 부모 노드의 키보다 작음
오른쪽 자식 노드의 키는 부모 노드의 키보다 큼
각각의 서브 트리도 이진 탐색 트리를 유지
중복된 키를 허용하지 않음
이진 탐색 트리의 특징
이진 탐색 트리 규칙에 의해 데이터가 정렬됨
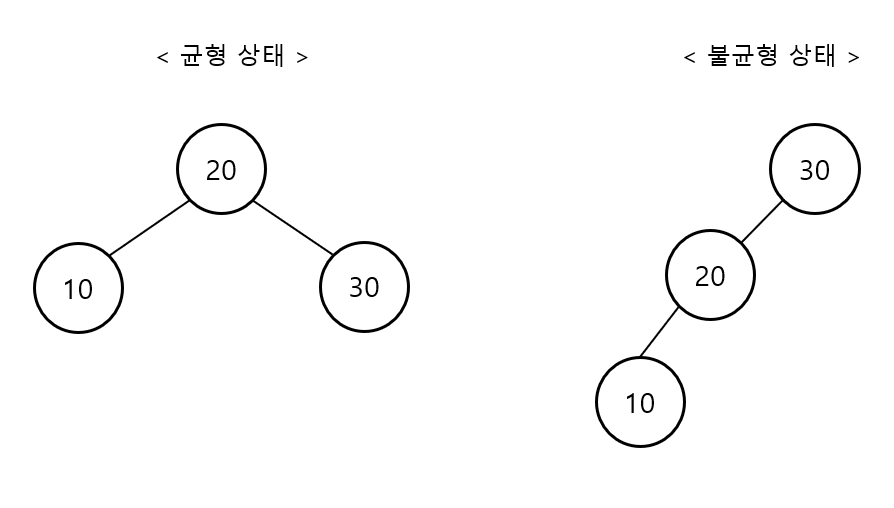
이진 트리에 비해 탐색 빠름 (균형 유지 필요)
균형 상태: O(logN)
불균형 상태: O(N)
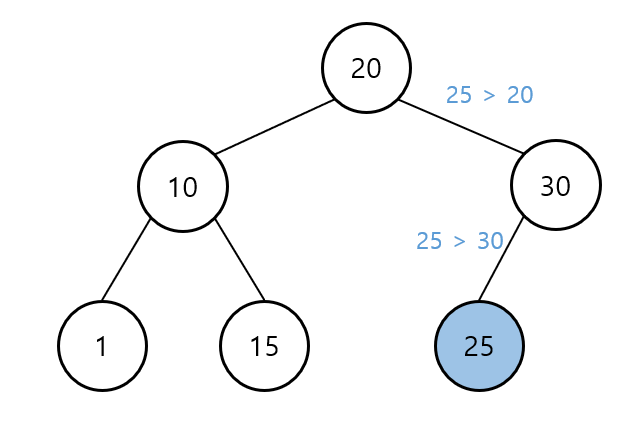
이진 탐색 트리 - 탐색
찾고자 하는 데이터를 루트 노드부터 비교 시작
대소 비교를 하여 찾는 데이터가 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽 노드로 이동
찾는 데이터가 없으면 null 반환
어떤 데이터를 찾더라도 최대 트리 높이 만큼의 탐색이 이루어짐
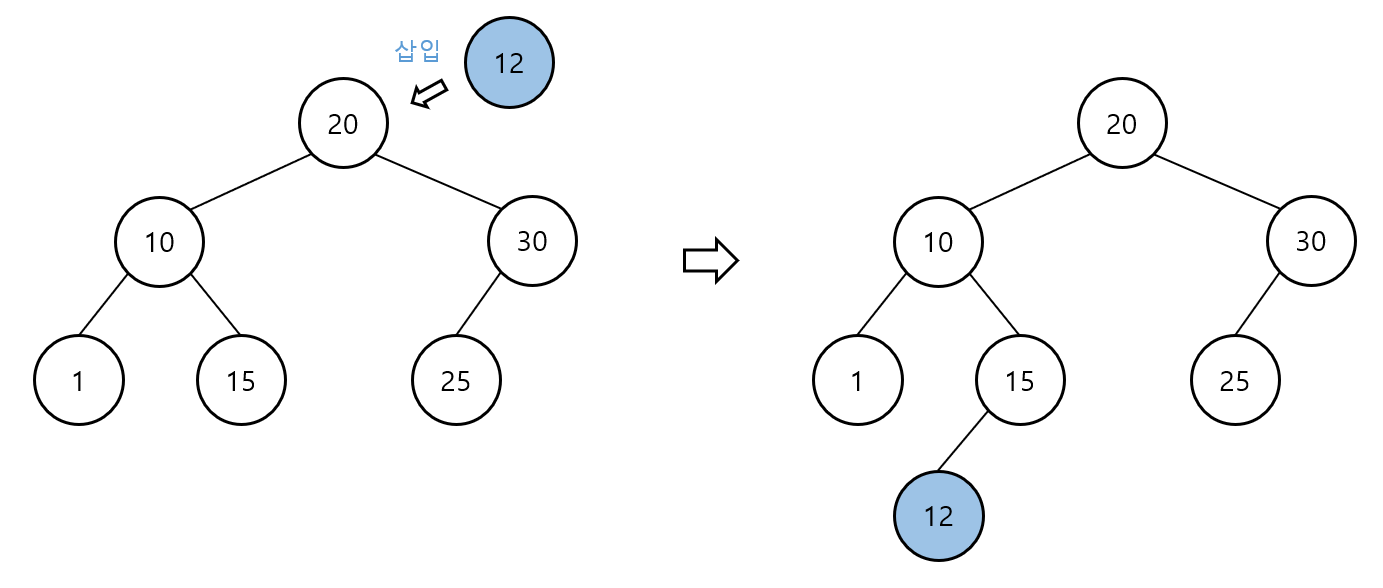
이진 탐색 트리 – 삽입
Root 부터 비교 시작 (중복 키 발견 시 노드 추가하지 않고 종료)
삽입할 키가 현재 노드의 키보다 작으면 왼쪽으로 이동
삽입할 키가 현재 노드의 키보다 크면 오른쪽으로 이동
Leaf 노드에 도달 후 키 비교하여 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽에 삽입
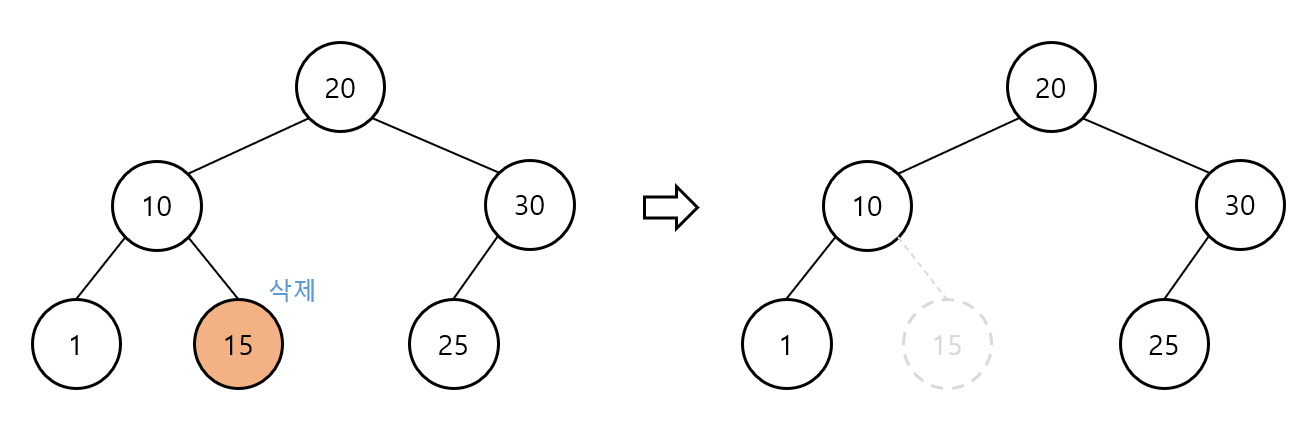
이진 탐색 트리 – 삭제(1)
삭제 대상 노드가 Leaf 노드인 경우
삭제 대상 노드 삭제
부모 노드의 해당 자식 링크 null로 변경
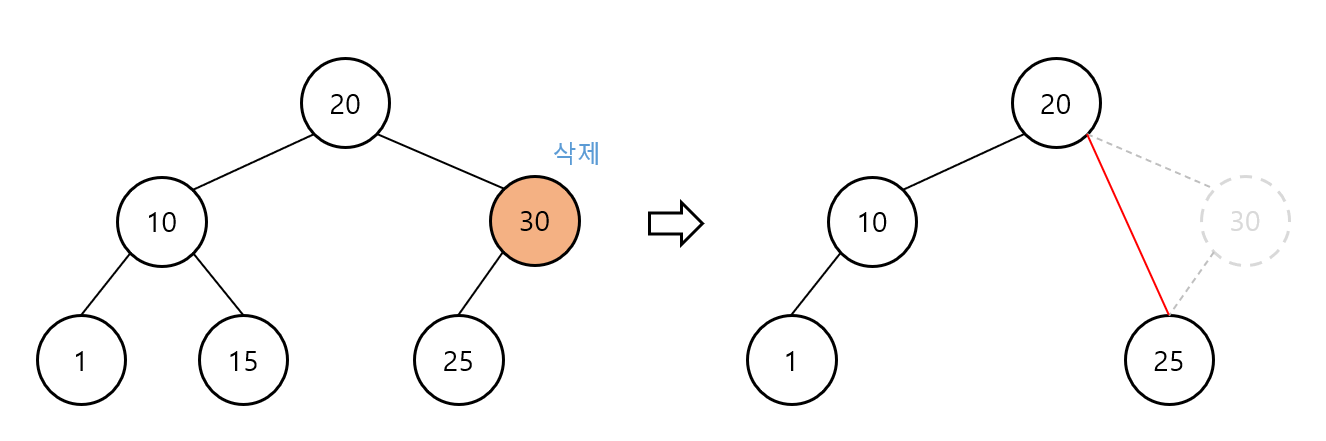
이진 탐색 트리 – 삭제(2)
삭제 대상 노드에 자식 노드가 하나 있는 경우
자식 노드를 삭제 대상 노드의 부모 노드에 연결
삭제 대상 노드 삭제
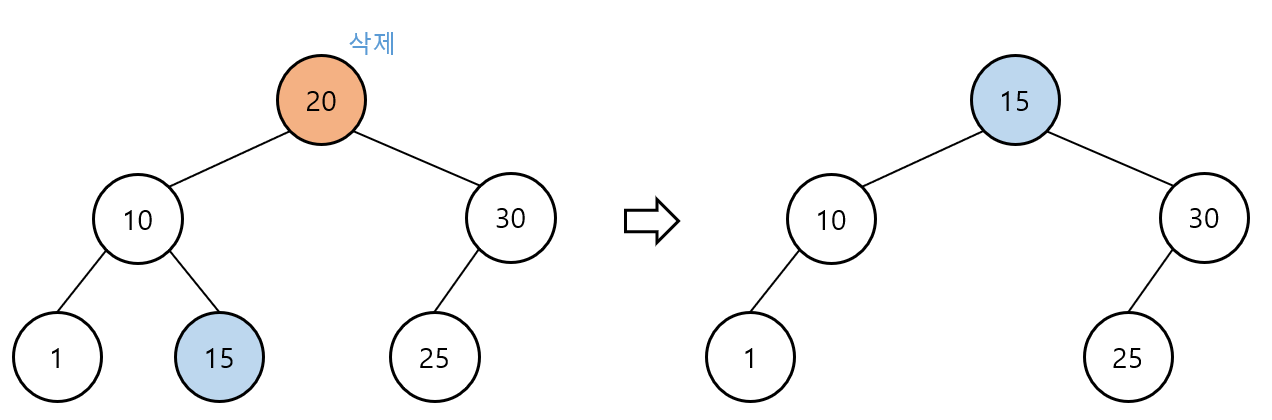
이진 탐색 트리 – 삭제(3)
삭제 대상 노드에 자식 노드가 둘인 경우
ⅰ삭제 대상 노드의 왼쪽 서브 트리에서 가장 큰 노드 선택
ⅱ삭제 대상 노드의 오른쪽 서브 트리에서 가장 작은 노드 선택
ⅰ또는 ⅱ에서 선택한 노드를 삭제 대상 노드 위치로 올림
위로 올리는 과정에서 다른 자식 노드들의 링크 연결 작업 진행
삭제 대상 노드 삭제
비선형 자료구조 - 이진 탐색 트리
// 비선형 자료구조 - 이진 탐색 트리
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int key, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
Node head;
BinarySearchTree(int key) {
this.head = new Node(key, null, null);
}
public void addNode(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(key, null, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (true) {
Node pre = cur;
if (key < cur.key) {
cur = cur.left;
if (cur == null) {
pre.left = new Node(key, null, null);
break;
}
} else {
cur = cur.right;
if (cur == null) {
pre.right = new Node(key, null, null);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public void removeNode(int key) {
Node parent = null;
Node successor = null;
Node predecessor = null;
Node child = null;
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (key == cur.key) {
break;
}
parent = cur;
if (key < cur.key) {
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
}
}
if (cur == null) {
System.out.println("key에 해당하는 노드가 없습니다.");
return;
}
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) { // Leaf 노드인 경우
if (parent == null) {
this.head = null;
} else {
if (parent.left == cur) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
}
} else if (cur.left != null && cur.right == null || cur.left == null && cur.right != null) { // 자식노드가 하나인 경우
if (cur.left != null) {
child = cur.left;
} else {
child = cur.right;
}
if (parent == null) {
this.head = child;
} else {
if (parent.left == cur) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
}
} else { // 자식이 둘인 경우
predecessor = cur;
successor = cur.left;
while (successor.right != null) {
predecessor = successor;
successor = successor.right;
}
predecessor.right = successor.left;
successor.left = cur.left;
successor.right = cur.right;
if (parent == null) {
this.head = successor;
} else {
if (parent.left == cur) {
parent.left = successor;
} else {
parent.right = successor;
}
}
}
}
public void levelOrder(Node node) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.key + " ");
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
// 노드 삽입
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree(20);
bst.addNode(10);
bst.addNode(30);
bst.addNode(1);
bst.addNode(15);
bst.addNode(25);
bst.addNode(13);
bst.addNode(35);
bst.addNode(27);
bst.addNode(40);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
// 노드 삭제
bst.removeNode(40);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
bst.removeNode(25);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
bst.removeNode(20);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
}
}
20 10 30 1 15 25 35 13 27 40
20 10 30 1 15 25 35 13 27
20 10 30 1 15 27 35 13
15 10 30 1 13 27 35
앞의 BST 삽입, 삭제 코드를 재귀 형태로 구현
// Practice1
// 앞의 BST 삽입, 삭제 코드를 재귀 형태로 구현
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class BinarySearchTree2 {
Node head;
BinarySearchTree2(int key) {
this.head = new Node(key, null, null);
}
public Node addNodeRecursive(Node cur, int key) {
if (cur == null) {
return new Node(key, null, null);
}
if (key < cur.key) {
cur.left = addNodeRecursive(cur.left, key);
} else {
cur.right = addNodeRecursive(cur.right, key);
}
return cur;
}
public Node removeNodeRecursive(Node cur, int key) {
if (cur == null) {
return null;
}
if (key < cur.key) {
cur.left = removeNodeRecursive(cur.left, key);
} else if (key > cur.key) {
cur.right = removeNodeRecursive(cur.right, key);
} else {
if (cur.left == null) {
return cur.right;
} else if (cur.right == null) {
return cur.left;
} else {
Node predecessor = cur;
Node successor = cur.left;
while (successor.right != null) {
predecessor = successor;
successor = successor.right;
}
predecessor.right = successor.left;
cur.key = successor.key;
}
}
return cur;
}
public void levelOrder(Node node) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.key + " ");
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
// 노드 삽입
BinarySearchTree2 bst = new BinarySearchTree2(20);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 10);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 30);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 1);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 15);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 25);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 13);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 35);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 27);
bst.head = bst.addNodeRecursive(bst.head, 40);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
// 노드 삭제
bst.head = bst.removeNodeRecursive(bst.head,40);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
bst.head = bst.removeNodeRecursive(bst.head, 25);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
bst.head = bst.removeNodeRecursive(bst.head, 20);
bst.levelOrder(bst.head);
}
}
20 10 30 1 15 25 35 13 27 40
20 10 30 1 15 25 35 13 27
20 10 30 1 15 27 35 13
15 10 30 1 13 27 35
문제 풀이
주어진 이진 탐색 트리에서 N 번째로 작은 수 구하기
// Practice1
// 주어진 이진 탐색 트리에서 N 번째로 작은 수 구하기
// 입력 트리: 3, 1, 4, null, 2
// N: 1
// 결과: 1
// 입력 트리: 5, 3, 6, 2, 4, null, null, 1
// N: 3
// 결과: 3
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int key, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
Node head;
BinarySearchTree() {}
BinarySearchTree(int key) {
this.head = new Node(key, null, null);
}
public void addNode(int key) {
this.head = this.addNode(this.head, key);
}
public Node addNode(Node cur, int key) {
if (cur == null) {
return new Node(key, null, null);
}
if (key < cur.key) {
cur.left = addNode(cur.left, key);
} else {
cur.right = addNode(cur.right, key);
}
return cur;
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(Integer[] data, int n) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree(data[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i] == null) {
continue;
}
bst.addNode(data[i]);
}
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
inOrder(bst.head, list);
System.out.println(list.get(n - 1));
}
public static void inOrder(Node node, ArrayList list) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
inOrder(node.left, list);
list.add(node.key);
inOrder(node.right, list);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
Integer[] data = {3, 1, 4, null, 2};
int n = 1;
solution(data, n);
data = new Integer[]{5, 3, 6, 2, 4, null, null, 1};
n = 3;
solution(data, n);
}
}
1
3
주어진 BST 에서 인접한 노드 간의 차이값 중 최소 값을 구하세요.
// Practice2
// 주어진 BST 에서 인접한 노드 간의 차이값 중 최소 값을 구하세요.
// 입력 트리: 4, 2, 6, 1, 3
// 출력: 1
// 입력 트리: 5, 1, 48, null, null, 12, 51
// 출력: 3
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(Integer[] data) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree(data[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i] == null) {
continue;
}
bst.addNode(data[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
levelOrder(bst.head, list);
int min = list.stream().min((x1, x2) -> x1 > x2 ? 1: -1).get();
// 참고2
min = Collections.min(list);
System.out.println(min);
}
public static void levelOrder(Node node, ArrayList list) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
list.add(Math.abs(cur.key - cur.left.key));
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
list.add(Math.abs(cur.key - cur.right.key));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
Integer[] data = {3, 1, 4, null, 2};
solution(data);
data = new Integer[]{5, 1, 48, null, null, 12, 51};
solution(data);
}
}
1
3
주어진 BST 에서 두 노드의 합이 target 값이 되는 경우가 있는지 확인.
// Practice3
// 주어진 BST 에서 두 노드의 합이 target 값이 되는 경우가 있는지 확인하세요.
// 있으면 true, 없으면 false 반환
// 입력 트리: 5, 3, 6, 2, 4, null, 7
// 결과: true
// 입력 트리: 5,3,6,2,4,null,7
// 결과: false
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution(Integer[] data, int target) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree(data[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i] == null) {
continue;
}
bst.addNode(data[i]);
}
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
boolean result = search(bst.head, set, target);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static boolean search(Node node, HashSet<Integer> set, int target){
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (set.contains(target - node.key)) {
return true;
}
set.add(node.key);
if (search(node.left, set, target)) {
return true;
}
if (search(node.right, set, target)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] data = {5, 3, 6, 2, 4, null, 7};
int target = 9;
solution(data, target);
data = new Integer[]{5,3,6,2,4,null,7};
target = 28;
solution(data, target);
}
}
true
false
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment