큐
큐 (Queue)
선입선출 (First In First Out; FIFO) 자료구조
먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 구조
입력 순서대로 데이터 처리가 필요할 때 사용
프린터 출력 대기열, BFS (Breath-First Search) 등
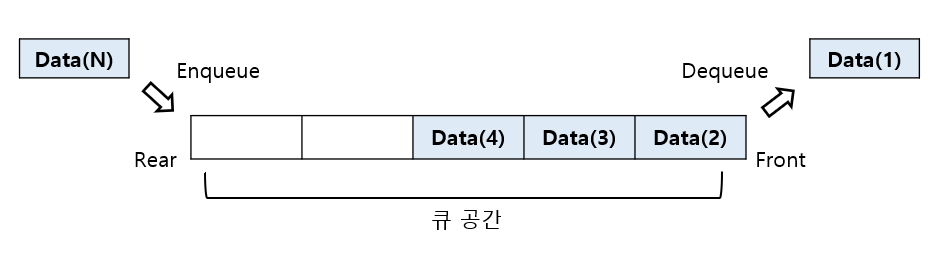
큐 기본 구조
선입선출 구조를 따름
기본적으로 데이터 추가, 꺼내기, 큐 공간 확인 동작으로 이루어짐
큐 기본 연산
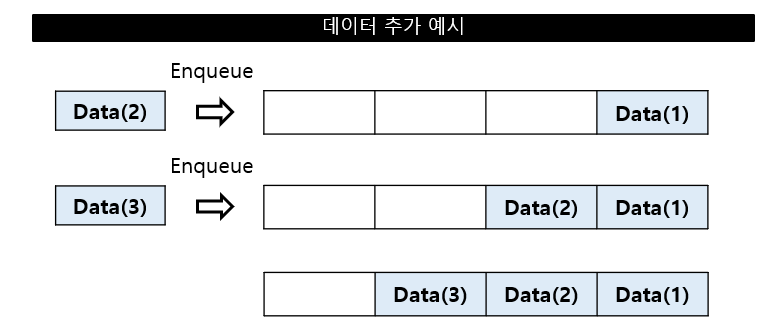
데이터 추가 (Enqueue)
큐에 데이터 추가
큐 기본 연산
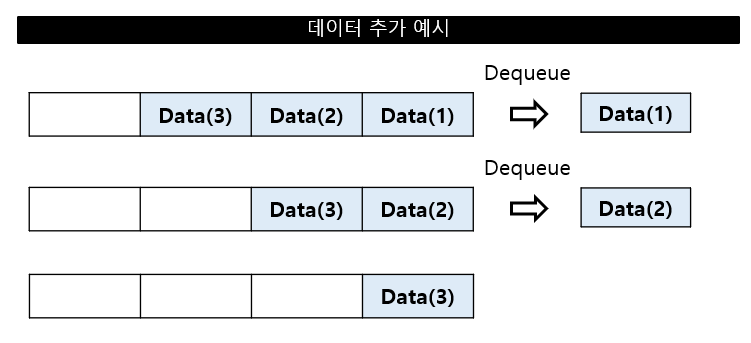
데이터 꺼내기 (Dequeue)
큐에서 데이터 꺼내기
선형 자료구조 - 큐
// 선형 자료구조 - 큐
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
queue.add(5);
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.contains(3));
System.out.println(queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
queue.clear();
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
1
[2, 3, 4, 5]
2
[3, 4, 5]
3
[3, 4, 5]
true
3
false
[]
null
ArrayList 를 이용한 큐 구현
// Practice1
// ArrayList 를 이용한 큐 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MyQueue1 {
ArrayList list;
MyQueue1() {
this.list = new ArrayList();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.list.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public void push(int data) {
this.list.add(data);
}
public Integer pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty!");
return null;
}
int data = (int)this.list.get(0);
this.list.remove(0);
return data;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty!");
return null;
}
return (int)this.list.get(0);
}
public void printQueue() {
System.out.println(this.list);
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyQueue1 myQueue = new MyQueue1();
myQueue.push(1);
myQueue.push(2);
myQueue.push(3);
myQueue.push(4);
myQueue.push(5);
myQueue.printQueue(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.peek()); // 1
myQueue.printQueue(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.pop()); // 1
myQueue.printQueue(); // 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.pop()); // 2
myQueue.printQueue(); // 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.pop());
System.out.println(myQueue.pop());
System.out.println(myQueue.pop());
myQueue.printQueue();
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
1
[2, 3, 4, 5]
2
[3, 4, 5]
3
4
5
[]
배열을 이용한 기본 큐 직접 구현 (원형 큐)
// Practice2
// 배열을 이용한 기본 큐 직접 구현 (원형 큐)
class MyQueue2 {
int[] arr;
int front = 0;
int rear = 0;
MyQueue2(int size) {
arr = new int[size + 1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.rear == this.front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (this.rear + 1) % this.arr.length == this.front;
}
public void enqueue(int data) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full!");
return;
}
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.arr.length;
this.arr[this.rear] = data;
}
public Integer dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty!");
return null;
}
front = (front + 1) % this.arr.length;
return this.arr[front];
}
public void printQueue() {
int start = (this.front + 1) % this.arr.length;
int end = (this.rear + 1) % this.arr.length;
for (int i = start; i != end; i = (i + 1) % this.arr.length) {
System.out.print(this.arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyQueue2 myQueue = new MyQueue2(5);
myQueue.enqueue(1);
myQueue.enqueue(2);
myQueue.enqueue(3);
myQueue.enqueue(4);
myQueue.enqueue(5);
myQueue.enqueue(6); // Queue is full!
myQueue.printQueue(); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 1
myQueue.printQueue(); // 2, 3, 4, 5
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 2
myQueue.printQueue(); // 3, 4, 5
myQueue.enqueue(6);
myQueue.enqueue(7);
myQueue.printQueue(); // 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 3
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 4
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 5
myQueue.printQueue(); // 6, 7
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 6
System.out.println(myQueue.dequeue()); // 7
myQueue.dequeue(); // Queue is empty!
}
}
Queue is full!
1 2 3 4 5
1
2 3 4 5
2
3 4 5
3 4 5 6 7
3
4
5
6 7
6
7
Queue is empty!
문제풀이
// Practice1
// 카드 섞기
// 1부터 N 까지의 번호로 구성된 N장의 카드가 있다.
// 1번 카드가 가장 위에 그리고 N번 카드는 가장 아래의 상태로 카드가 순서대로 쌓여있다.
// 아래의 동작을 카드 한 장만 남을 때까지 반복했을 때, 가장 마지막 남는 카드 번호를 출력하시오.
// 1. 가장 위의 카드는 버린다.
// 2. 그 다음 위의 카드는 쌓여 있는 카드의 가장 아래에 다시 넣는다.
// 예시 입력)
// N = 4
// 결과: 4
// N = 7
// 결과: 6
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Practice1 {
public static int findLastCard(int N) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
IntStream.range(1, N + 1).forEach(x -> queue.add(x));
System.out.println(queue);
while (queue.size() > 1) {
queue.remove();
int data = (int)queue.remove();
queue.add(data);
System.out.println(queue);
}
return (int)queue.remove();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(findLastCard(4)); // 4
System.out.println(findLastCard(7)); // 6
System.out.println(findLastCard(9)); // 2
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[3, 4, 2]
[2, 4]
[4]
4
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2]
[5, 6, 7, 2, 4]
[7, 2, 4, 6]
[4, 6, 2]
[2, 6]
[6]
6
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 2]
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 2, 4]
[7, 8, 9, 2, 4, 6]
[9, 2, 4, 6, 8]
[4, 6, 8, 2]
[8, 2, 6]
[6, 2]
[2]
2
// Practice2
// 요세푸스 문제
// N과 K가 주어졌을 때 (N, K) 요세푸스 순열을 구하시오.
// N과 K는 N >= K 를 만족하는 양의 정수이다.
// 1부터 N 번까지 N명이 순서대로 원을 이루어 모여 있다.
// 이 모임에서 원을 따라 순서대로 K번째 사람을 제외한다.
// 모든 사람이 제외될 때까지 반복하며 이 때, 제외되는 순서가 요세푸스 순열이다.
// 예시 입력
// 입력: N = 5, K = 2
// 결과: 2, 4, 1, 5, 3
// 입력: N = 7, K = 3
// 결과: 3, 6, 2, 7, 5, 1, 4
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Practice2 {
public static ArrayList getJosephusPermutation(int N, int K) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
ArrayList result = new ArrayList();
IntStream.range(1, N + 1).forEach(x -> queue.add(x));
int cnt = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int data = (int)queue.remove();
cnt += 1;
if (cnt % K == 0) {
result.add(data);
} else {
queue.add(data);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(getJosephusPermutation(5, 2));
System.out.println(getJosephusPermutation(7, 3));
}
}
[2, 4, 1, 5, 3]
[3, 6, 2, 7, 5, 1, 4]
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment