해시 테이블
해시 테이블 (Hash Table) = 해시 맵, 해시 표
키 (Key), 값 (Value)을 대응시켜 저장하는 데이터 구조
키를 통해 해당 데이터에 빠르게 접근 가능
해싱
키를 특정 계산식에 넣어 나온 결과를 사용하여 값에 접근하는 과정
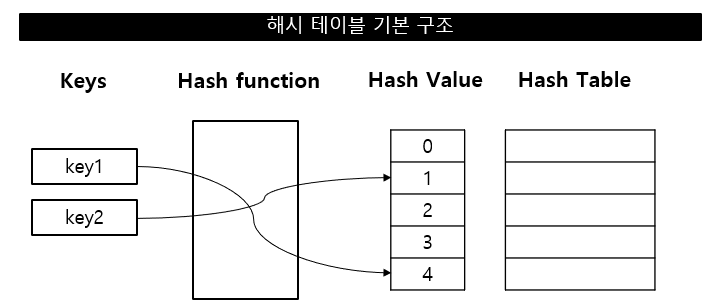
해시 테이블 구조
키: 해시 테이블 접근을 위한 입력 값
해시 함수: 키를 해시 값으로 매핑하는 연산
해시 값: 해시 테이블의 인덱스
해시 테이블: 키-값을 연관시켜 저장하는 데이터 구조
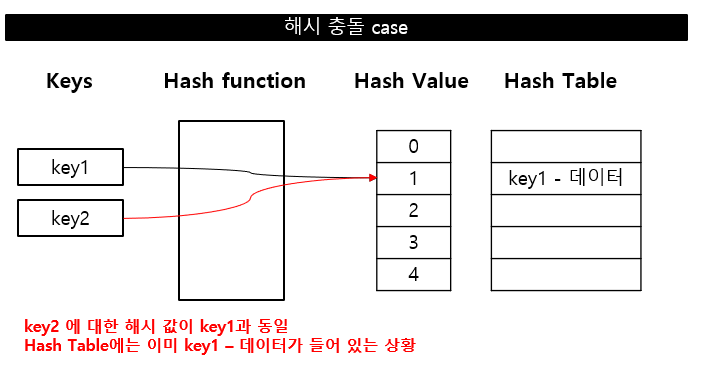
해시 충돌
해시 테이블의 같은 공간에 서로 다른 값을 저장하려는 경우
서로 다른 키의 해시 함수를 통한 해시 값이 동일한 경우
해시 충돌 해결 방법으로는 크게 개방 주소법과 분리 연결법 이 있음
해시 충돌 해결 방법 (1)
개방 주소법 (Open Address)
충돌 시, 테이블에서 비어 있는 공간의 hash를 찾아 데이터를 저장
hash와 value가 1:1 관계 유지
비어 있는 공간 탐색 방법에 따라 분류
선형 탐사법, 제곱 탐사법, 이중 해싱
개방 주소법 – 선형 탐사법
Linear Probing
빈 공간을 순차적으로 탐사하는 방법
충돌 발생 지점 부터 이후의 빈 공간을 순서대로 탐사
일차 군집화 문제 발생
반복된 충돌 발생 시 해당 지점 주변에 데이터가 몰리는 경우 발생
개방 주소법 – 제곱 탐사법
Quadratic Probing
빈 공간을 n제곱만큼의 간격을 두고 탐사하는 방법
충돌 발생 지점 부터 이후의 빈 공간을 n제곱 간격으로 탐사
일차 군집화 문제 일부 보완
이차 군집화 문제 발생 가능성
개방 주소법 – 이중 해싱
Double Hashing
해싱 함수를 이중으로 사용
해시 함수 1: 최초 해시를 구할 때 사용
해시 함수 2: 충돌 발생 시, 탐사 이동 간격을 구할 때 사용
선형 탐사, 제곱 탐사에 비해 데이터가 골고루 분포됨
해시 충돌 해결 방법 (2)
분리 연결법 (Separate Chaining)
해시 테이블을 연결 리스트로 구성
충돌 발생 시, 테이블 내의 다른 위치를 탐색하는 것이 아닌 연결 리스트를 이용하여 해당 테이블에 데이터를 연결
선형 자료구조 - 해시 테이블
// 선형 자료구조 - 해시 테이블
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
// 해시 함수
public static int getHash(int key) {
return key % 5;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 기본 해시 테이블 사용 방법
Hashtable<String, Integer> ht = new Hashtable();
ht.put("key1", 10);
ht.put("key2", 20);
ht.put("key3", 30);
// ht.put("key3", 40);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> item: ht.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
System.out.println(ht.get("key1"));
System.out.println(ht.get("key2"));
ht.remove("key1");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> item: ht.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
// 해시 충돌 케이스 (해시 함수 사용)
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht2 = new Hashtable();
ht2.put(getHash(1), 10);
ht2.put(getHash(2), 20);
ht2.put(getHash(3), 30);
ht2.put(getHash(4), 40);
ht2.put(getHash(5), 50);
System.out.println("== 충돌 전 ==");
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item: ht2.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
System.out.println("== 충돌 후 ==");
ht2.put(getHash(6), 60);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item: ht2.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(item.getKey() + " - " + item.getValue());
}
}
}
key3 - 30
key2 - 20
key1 - 10
10
20
key3 - 30
key2 - 20
== 충돌 전 ==
4 - 40
3 - 30
2 - 20
1 - 10
0 - 50
== 충돌 후 ==
4 - 40
3 - 30
2 - 20
1 - 60
0 - 50
해시 테이블 배열로 직접 구현
// Practice1
// 해시 테이블 배열로 직접 구현
class MyHashTable {
Integer[] table;
int elemCnt;
MyHashTable() {}
MyHashTable(int size) {
this.table = new Integer[size];
this.elemCnt = 0;
}
public int getHash(int key) {
return key % this.table.length;
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx] = data;
this.elemCnt++;
}
public int getValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
return this.table[idx];
}
public void removeValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx] = null;
this.elemCnt--;
}
public void printHashTable() {
System.out.println("== Hash Table ==");
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + ": " + this.table[i]);
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable ht = new MyHashTable(7);
ht.setValue(1, 1);
ht.setValue(2, 2);
ht.setValue(3, 3);
ht.setValue(4, 4);
ht.setValue(5, 5);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(8, 6);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: 2
3: 3
4: 4
5: 5
6: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 6
2: 2
3: 3
4: 4
5: 5
6: null
해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (선형 탐사법)
// Practice2
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (선형 탐사법)
class MyHashTable2 extends MyHashTable {
MyHashTable2(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) {
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) {
this.table[idx] = data;
} else {
int newIdx = idx;
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + 1) % this.table.length;
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) {
break;
}
}
this.table[newIdx] = data;
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable2 ht = new MyHashTable2(5);
ht.setValue(1, 1);
ht.setValue(3, 3);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 20);
ht.setValue(1, 30);
ht.setValue(1, 40);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: null
3: 3
4: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 1
2: 10
3: 3
4: null
Hash table is full!
== Hash Table ==
0: 30
1: 1
2: 10
3: 3
4: 20
해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (제곱 탐사법)
// Practice3
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (제곱 탐사법)
class MyHashTable3 extends MyHashTable {
MyHashTable3(int size) {
super(size);
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) {
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) {
this.table[idx] = data;
} else {
int newIdx = idx;
int cnt = 0;
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + (int)Math.pow(2, cnt)) % this.table.length;
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) {
break;
}
cnt++;
}
this.table[newIdx] = data;
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable3 ht = new MyHashTable3(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(4, 40);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 100);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 200);
ht.setValue(1, 300);
ht.setValue(1, 400);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: null
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: 100
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: null
4: 40
5: 200
6: null
7: null
8: 100
9: 400
10: 300
해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (이중 해싱)
// Practice4
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 개방 주소법 (이중 해싱)
class MyHashTable4 extends MyHashTable {
int c;
MyHashTable4(int size) {
super(size);
this.c = this.getHashC(size);
}
public int getHashC(int size) {
int c = 0;
if (size <= 2) {
return size;
}
for (int i = size - 1; i > 2; i--) {
boolean isPrime = true;
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) {
if (i % j == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) {
c = i;
break;
}
}
return c;
}
public int getHash2(int key) {
int hash = 1 + key % this.c;
return hash;
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
if (this.elemCnt == this.table.length) {
System.out.println("Hash table is full!");
return;
} else if (this.table[idx] == null) {
this.table[idx] = data;
} else {
int newIdx = idx;
int cnt = 1;
while (true) {
newIdx = (newIdx + this.getHash2(newIdx) * cnt) % this.table.length;
if (this.table[newIdx] == null) {
break;
}
cnt++;
}
this.table[newIdx] = data;
}
elemCnt++;
}
}
public class Practice4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable4 ht = new MyHashTable4(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(3, 30);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(1, 100);
ht.setValue(1, 200);
ht.setValue(1, 300);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
== Hash Table ==
0: null
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: null
5: null
6: null
7: null
8: null
9: null
10: null
== Hash Table ==
0: 100
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: null
5: null
6: null
7: 300
8: 200
9: null
10: null
해시 충돌 해결 - 분리 연결법
// Practice5
// 해시 충돌 해결 - 분리 연결법
class Node {
int key;
int data;
Node next;
Node() {}
Node(int key, int data, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList() {}
LinkedList(Node node) {
this.head = node;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void addData(int key, int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new Node(key, data, null);
} else {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new Node(key, data, null);
}
}
public void removeData(int data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
Node pre = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == data) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = cur.next;
} else {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public Integer findData(int key) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return null;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == key) {
return cur.data;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("Data not found!");
return null;
}
public void showData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is empty!");
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class MyHashTable5 {
LinkedList[] table;
MyHashTable5(int size) {
this.table = new LinkedList[size];
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
this.table[i] = new LinkedList(null);
}
}
public int getHash(int key) {
return key % this.table.length;
}
public void setValue(int key, int data) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx].addData(key, data);
}
public int getValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
int data = this.table[idx].findData(key);
return data;
}
public void removeValue(int key) {
int idx = this.getHash(key);
this.table[idx].removeData(key);
}
public void printHashTable() {
System.out.println("== Hash Table ==");
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": ");
this.table[i].showData();
}
}
}
public class Practice5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MyHashTable5 ht = new MyHashTable5(11);
ht.setValue(1, 10);
ht.setValue(2, 20);
ht.setValue(3, 30);
ht.printHashTable();
ht.setValue(12, 11);
ht.setValue(23, 12);
ht.setValue(34, 13);
ht.setValue(13, 21);
ht.setValue(24, 22);
ht.setValue(35, 23);
ht.setValue(5, 1);
ht.setValue(16, 2);
ht.setValue(27, 3);
ht.printHashTable();
System.out.println("== key 값으로 해당 데이터 가져오기 ==");
System.out.println(ht.getValue(1));
System.out.println(ht.getValue(12));
System.out.println("== 데이터 삭제 ==");
ht.removeValue(1);
ht.removeValue(5);
ht.removeValue(16);
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 10
2: 20
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: List is empty!
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 10 11 12 13
2: 20 21 22 23
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: 1 2 3
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!
== key 값으로 해당 데이터 가져오기 ==
10
11
== 데이터 삭제 ==
== Hash Table ==
0: List is empty!
1: 11 12 13
2: 20 21 22 23
3: 30
4: List is empty!
5: 3
6: List is empty!
7: List is empty!
8: List is empty!
9: List is empty!
10: List is empty!
문제 풀이
해시 테이블을 이용한 수 찾기
// Practice1
// 해시 테이블을 이용한 수 찾기
// 주어진 첫 번째 배열을 이용하여 해시 테이블을 초기화 한 후
// 두 번째 배열이 주어졌을 때 해당 배열 내 데이터가 해시 테이블에 있는지 확인하는 코드를 작성하세요.
// 입출력 예시)
// 배열1: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
// 배열2: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
// 출력: True, False, True, False, True
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>();
// 해시 테이블 구성
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
ht.put(arr1[i], arr1[i]);
}
// 포함하고 있으면 true, 없으면 false 출력
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
if(ht.containsKey(arr2[i])) {
System.out.print("True ");
} else {
System.out.print("False ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr1 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
solution(arr1, arr2);
}
}
True False True False True
임의의 두 수를 더해 target 확인하는 프로그램
// Practice2
// 정수형 배열 nums 와 target 이 주어졌을 때,
// nums 에서 임의의 두 수를 더해 target 을 구할 수 있는지 확인하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 두 수 의 합으로 target 을 구할 수 있으면 해당 값의 index 를 반환하고,
// 없는 경우 null 을 반환하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// nums: 7, 11, 5, 3
// target: 10
// 출력: 0, 3
// nums: 8, 3, -2
// target: 6
// 출력: 0, 2
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Practice2 {
public static int[] solution(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>();
// 해시 테이블을 full 로 구성하고 시작 x
// 현재 값이 해시테이블에 있는지 검사
// 있으면 구간 result 에 설정 후 break
// 없으면 target - 현재 값 을 해시 테이블에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (ht.containsKey(numbers[i])) {
result[0] = ht.get(numbers[i]);
result[1] = i;
return result;
}
ht.put(target - numbers[i], i);
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {7, 11, 5, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 10)));
nums = new int[]{8, 3, -2};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 6)));
nums = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(nums, 12)));
}
}
[0, 3]
[0, 2]
null
참고 - Hashtable? HashMap?
// Practice3
// 참고 - Hashtable? HashMap?
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class Practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Hashtable
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> ht = new Hashtable<>();
ht.put(0, 10);
System.out.println(ht.get(0));
// HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put(0, 10);
System.out.println(hm.get(0));
// Map 인터페이스 (다형성)
Map<Integer, Integer> map1 = ht;
Map<Integer, Integer> map2 = hm;
System.out.println(map1.get(0));
System.out.println(map2.get(0));
// ht.put(null, -999);
// System.out.println(ht.get(null));
hm.put(null, -999);
System.out.println(hm.get(null));
// Hashtable 과 HashMap 차이
// 공통: 둘 다 Map 인터페이스를 구현한 것
// 차이:
// Thread-safe
// Hashtable: O (멀티 스레드 환경에서 우수)
// HashMap: X (싱글 스레드 환경에서 우수)
// 참고) synchronizedMap, ConcurrentHashMap
// Key 에 Null 사용 여부
// Hashtable: X
// HashMap: O
}
}
10
10
10
10
-999
출처 : 제로베이스

Leave a comment