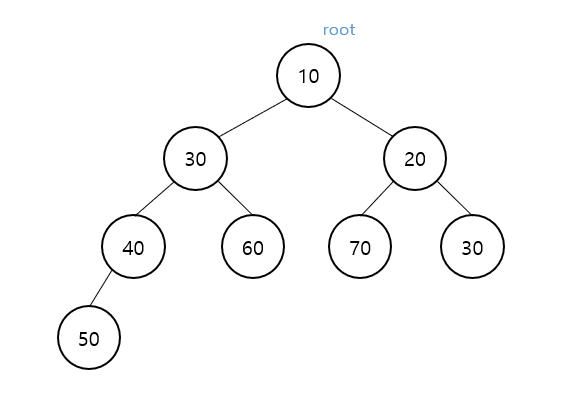
힙
힙 (Heap)
완전 이진 트리 형태
중복 값 허용
반 정렬 상태
최소값 또는 최대값을 빠르게 찾아내는데 유용한 자료구조
최소 힙, 최대 힙
최소 힙 (Min Heap)
부모 노드의 키가 자식 노드의 키보다 작거나 같은 형태
최대 힙 (Max Heap)
부모 노드의 키가 자식 노드의 키보다 크거나 같은 형태
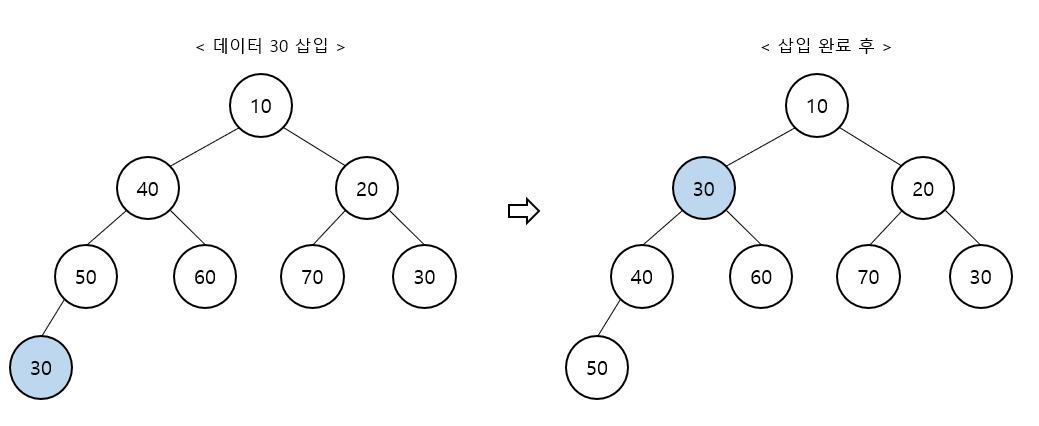
최소 힙 - 삽입
트리의 가장 끝 위치에 데이터 삽입
부모 노드와 키 비교한 후 작을 경우 부모 자리와 교체 (반복)
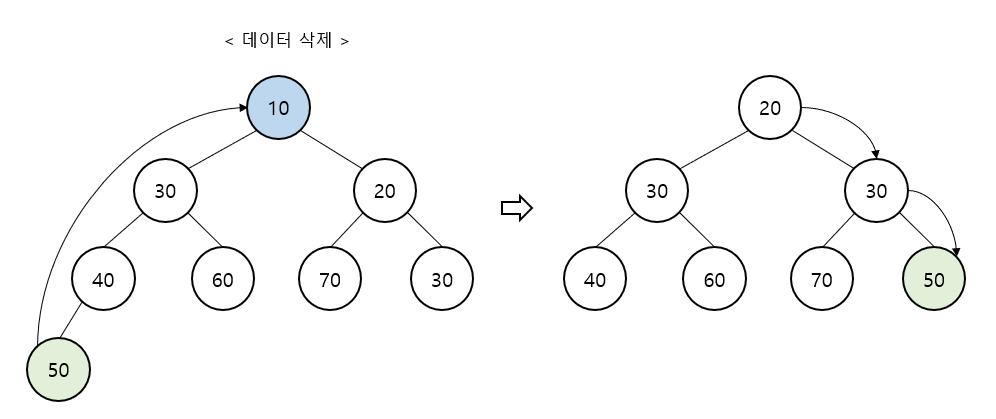
최소 힙 - 삭제
최상위 노드 반환 및 삭제
가장 마지막 위치의 노드를 최상위 노드로 위치 시킴
자식 노드 중 작은 값과 비교 후 부모 노드가 더 크면 자리 교체 (반복)
ArrayList 로 최소 힙 구현
// 비선형자료구조 - 힙
// ArrayList 로 최소 힙 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MinHeap {
ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public MinHeap() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(0); //더미 데이터를 넣어 인덱스 1번부터 시작할수 있게 끔함.
}
public void insert(int data) {
// 가장 끝 위치에 데이터 추가
heap.add(data);
// 추가한 후 부모와 크기 비교하며 자기 자리 찾아가기
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
//cur > 1 1보다는 커야 부모노드가 존재하니까!
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) > heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, data); //부모쪽 데이터에는 방금 들어온 데이터를 넣어줌.
heap.set(cur, parentVal); // 자식쪽 데이터에는 부모의 데이터를 넣어줌.
cur /= 2; //현재 위치를 부모쪽으로 바꿔줌.
//이과정을 반복해서 삽입한 데이터를 맞는 노드위치에 위치시킴.
}
}
//삭제 하는 노드값 반환해야 하므로 반환값 타입 Integer로 설정!
public Integer delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty!");
return null;
}
// delete 대상 노드는 가장 상위 노드
//1번째 위치가 가장 상위 노드임.
int target = heap.get(1);
// 마지막 노드를 가장 위로 설정 후 마지막 노드는 삭제
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1)); //가장 위 노드를 삭제하고, 마지막 노드를 가져와서 넣어줌.
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);// 가장위로 설정된 마지막 노드는 삭제해줌.
int cur = 1; //현재 위치를 최상위 노드로 설정.
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
//오른쪽 자식노드의 인덱스 값이 heap.size()보다 작아야 값이 있으니까!
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) { // 자식 노드 둘다 있는 경우
//자식 노드 둘다 있으니까 오른쪽 왼쪽 둘다 비교해서 위치선정해야함.
//비교할 자식 노드 값이 같을경우, 삼항연산자에서, 왼쪽 기준으로 오른쪽보다 작니 했을때 작지 않으니까 오른쪽값이 나옴.
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) < heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) { // 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있는 경우
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
//자식노드가 없는 상황, 부모노드 밖에 없는 상황 이거나, 더이상 비교할 대상이 없어서 break해주면됨.
break;
}
//이제 선정한 값을 부모노드와 비교해 주면됨!
if (heap.get(cur) < heap.get(targetIdx)) { // 부모가 작으면 종료
break;
} else { // 부모가 더 크면 자리 바꾸기
int parentVal = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
//값 변경해주고 또 그자리에서 문제가 있으면 또 다시 바꿔줘야 하므로 cur를 변경한 targetIdx위치로 바꿔줌.
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
//삭제도 하고 반환도 할꺼니까 리턴으로 해당 타켓값을 반환, 타겟값은 처음 꺼내왔던 값.
return target;
}
public void printTree() {
//0번째 더미데이터를 빼고 출력하기 위해 1부터 시작함.
for (int i = 1; i < this.heap.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.heap.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap();
System.out.println("== 데이터 삽입 ==");
minHeap.insert(30);
minHeap.insert(40);
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.printTree();
minHeap.insert(50);
minHeap.insert(60);
minHeap.insert(70);
minHeap.printTree();
minHeap.insert(20);
minHeap.printTree();
minHeap.insert(30);
minHeap.printTree();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== 데이터 삭제 ==");
System.out.println("삭제: " + minHeap.delete());
minHeap.printTree();
System.out.println("삭제: " + minHeap.delete());
minHeap.printTree();
System.out.println("삭제: " + minHeap.delete());
minHeap.printTree();
}
}
== 데이터 삽입 ==
10 40 30
10 40 30 50 60 70
10 40 20 50 60 70 30
10 30 20 40 60 70 30 50
== 데이터 삭제 ==
삭제: 10
20 30 30 40 60 70 50
삭제: 20
30 30 50 40 60 70
삭제: 30
30 40 50 70 60
ArrayList 로 최대 힙 구현
// Practice 1
// 최소 힙에서 특정 값을 변경하는 코드를 작성하세요.
// 특정 값이 여러개라면 모두 바꿔주세요.
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MinHeap{
ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public MinHeap() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(0);
}
public void insert(int data) {
// 가장 끝 위치에 데이터 추가
heap.add(data);
// 추가한 후 부모와 크기 비교하며 자기 자리 찾아가기
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) > heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, data);
heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public Integer delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty!");
return null;
}
// delete 대상 노드는 가장 상위 노드
int target = heap.get(1);
// 마지막 노드를 가장 위로 설정 후 마지막 노드는 삭제
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int cur = 1;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) { // 자식 노드 둘다 있는 경우
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) < heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) { // 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있는 경우
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (heap.get(cur) < heap.get(targetIdx)) { // 부모가 작으면 종료
break;
} else { // 부모가 더 크면 자리 바꾸기
int parentVal = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
return target;
}
public void printTree() {
for (int i = 1; i < this.heap.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.heap.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(MinHeap minHeap, int from, int to) {
for (int i = 1; i < minHeap.heap.size(); i++) {
if (minHeap.heap.get(i) == from) { // 변경할 값 발견
minHeap.heap.set(i, to); // 값 변경
//값 변경후, 힙 구조에 따라 값을 올리거나 내리는 작업해줘야함.
//별도 조건문 안써도 바꿀게 있으면 바꿔주기 때문에 이렇게만 작성해줘도 문제 없음.
moveUp(minHeap, i);
moveDown(minHeap, i);
}
}
}
public static void moveUp(MinHeap minHeap, int idx) {
//변경할 현재 노드를 가져옴.
int cur = idx;
//부모 노드의 값이 더 크면 현재 노드랑 바꿔주는 작업 반복해줌.
while (cur > 1 && minHeap.heap.get(cur / 2) > minHeap.heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = minHeap.heap.get(cur / 2);
minHeap.heap.set(cur / 2, minHeap.heap.get(cur));
minHeap.heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public static void moveDown(MinHeap minHeap, int idx) {
//변경할 현재 노드를 가져옴.
int cur = idx;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < minHeap.heap.size()) { // 자식 노드 둘다 있는 경우
targetIdx = minHeap.heap.get(leftIdx) < minHeap.heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < minHeap.heap.size()) { // 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있는 경우
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (minHeap.heap.get(cur) < minHeap.heap.get(targetIdx)) { // 부모가 작으면 종료
break;
} else { // 부모가 더 크면 자리 바꾸기
int parentVal = minHeap.heap.get(cur);
minHeap.heap.set(cur, minHeap.heap.get(targetIdx));
minHeap.heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.insert(30);
minHeap.insert(40);
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.insert(50);
minHeap.insert(60);
minHeap.insert(70);
minHeap.insert(20);
minHeap.insert(30);
System.out.println("== 데이터 변경 전 ==");
minHeap.printTree();
System.out.println("== 데이터 변경 후 ==");
solution(minHeap, 30, 100);
minHeap.printTree();
solution(minHeap, 60, 1);
minHeap.printTree();
}
}
== 데이터 삽입 ==
40 30 10
70 50 60 30 40 10
70 50 60 30 40 10 20
70 50 60 30 40 10 20 30
== 데이터 삭제 ==
삭제: 70
60 50 30 30 40 10 20
삭제: 60
50 40 30 30 20 10
삭제: 50
40 30 30 10 20
최소 힙에서 특정 값을 변경하는 코드
// Practice 1
// 최소 힙에서 특정 값을 변경하는 코드를 작성하세요.
// 특정 값이 여러개라면 모두 바꿔주세요.
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MinHeap{
ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public MinHeap() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(0);
}
public void insert(int data) {
// 가장 끝 위치에 데이터 추가
heap.add(data);
// 추가한 후 부모와 크기 비교하며 자기 자리 찾아가기
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) > heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, data);
heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public Integer delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty!");
return null;
}
// delete 대상 노드는 가장 상위 노드
int target = heap.get(1);
// 마지막 노드를 가장 위로 설정 후 마지막 노드는 삭제
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int cur = 1;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) { // 자식 노드 둘다 있는 경우
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) < heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) { // 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있는 경우
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (heap.get(cur) < heap.get(targetIdx)) { // 부모가 작으면 종료
break;
} else { // 부모가 더 크면 자리 바꾸기
int parentVal = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
return target;
}
public void printTree() {
for (int i = 1; i < this.heap.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.heap.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void solution(MinHeap minHeap, int from, int to) {
for (int i = 1; i < minHeap.heap.size(); i++) {
if (minHeap.heap.get(i) == from) { // 변경할 값 발견
minHeap.heap.set(i, to); // 값 변경
moveUp(minHeap, i);
moveDown(minHeap, i);
}
}
}
public static void moveUp(MinHeap minHeap, int idx) {
int cur = idx;
while (cur > 1 && minHeap.heap.get(cur / 2) > minHeap.heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = minHeap.heap.get(cur / 2);
minHeap.heap.set(cur / 2, minHeap.heap.get(cur));
minHeap.heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public static void moveDown(MinHeap minHeap, int idx) {
int cur = idx;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < minHeap.heap.size()) { // 자식 노드 둘다 있는 경우
targetIdx = minHeap.heap.get(leftIdx) < minHeap.heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < minHeap.heap.size()) { // 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있는 경우
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (minHeap.heap.get(cur) < minHeap.heap.get(targetIdx)) { // 부모가 작으면 종료
break;
} else { // 부모가 더 크면 자리 바꾸기
int parentVal = minHeap.heap.get(cur);
minHeap.heap.set(cur, minHeap.heap.get(targetIdx));
minHeap.heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.insert(30);
minHeap.insert(40);
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.insert(50);
minHeap.insert(60);
minHeap.insert(70);
minHeap.insert(20);
minHeap.insert(30);
System.out.println("== 데이터 변경 전 ==");
minHeap.printTree();
System.out.println("== 데이터 변경 후 ==");
solution(minHeap, 30, 100);
minHeap.printTree();
solution(minHeap, 60, 1);
minHeap.printTree();
}
}
== 데이터 변경 전 ==
10 30 20 40 60 70 30 50
== 데이터 변경 후 ==
10 40 20 50 60 70 100 100
1 10 20 50 40 70 100 100
최소 힙, 최대 힙을 이용하여 데이터를 오름차순, 내림차순으로 출력
// Practice 2
// 최소 힙, 최대 힙을 이용하여 데이터를 오름차순, 내림차순으로 출력해보세요.
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MaxHeap{
ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public MaxHeap() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(0);
}
public void insert(int data) {
heap.add(data);
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2) < heap.get(cur)) {
int parentVal = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, data);
heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public Integer delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty!");
return null;
}
int target = heap.get(1);
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int cur = 1;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) {
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx) > heap.get(rightIdx) ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) {
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (heap.get(cur) > heap.get(targetIdx)) {
break;
} else {
int parentVal = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
return target;
}
public void printTree() {
for (int i = 1; i < this.heap.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(this.heap.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(MinHeap minHeap) {
MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
System.out.print("오름차순: ");
while(minHeap.heap.size() != 1) {
int data = minHeap.delete();
System.out.print(data + " ");
maxHeap.insert(data);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("내림차순: ");
while (maxHeap.heap.size() != 1) {
System.out.print(maxHeap.delete() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.insert(30);
minHeap.insert(40);
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.insert(50);
minHeap.insert(60);
minHeap.insert(70);
minHeap.insert(20);
minHeap.insert(30);
solution(minHeap);
}
}
오름차순: 10 20 30 30 40 50 60 70
내림차순: 70 60 50 40 30 30 20 10
정수들을 힙 자료구조에 추가하고 n번 삭제 후 절대값이 큰 값부터 출력
// Practice 3
// 정수들을 힙 자료구조에 추가하고 n번 삭제 후 절대값이 큰 값부터 출력하세요.
// 입력: 3 0 -2 -5 9 6 -11, 20, -30
// 삭제 횟수: 1
// 출력: 20, -11 9 6 -5 3 -2 0
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
class Num {
int val;
boolean isMinus;
public Num(int val) {
// 음수인 경우 하기와 같이 체크
this.isMinus = val < 0 ? true : false;
// 값은 절대 값으로 넣기
this.val = Math.abs(val);
}
}
class MaxHeap2{
// Num으로 변경
ArrayList<Num> heap;
public MaxHeap2() {
this.heap = new ArrayList<>();
this.heap.add(new Num(0));
}
public void insert(int data) {
heap.add(new Num(data));
int cur = heap.size() - 1;
while (cur > 1 && heap.get(cur / 2).val < heap.get(cur).val) {
Num parentVal = heap.get(cur / 2);
heap.set(cur / 2, heap.get(cur));
heap.set(cur, parentVal);
cur /= 2;
}
}
public Num delete() {
if (heap.size() == 1) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty!");
return null;
}
Num target = heap.get(1);
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int cur = 1;
while (true) {
int leftIdx = cur * 2;
int rightIdx = cur * 2 + 1;
int targetIdx = -1;
if (rightIdx < heap.size()) {
targetIdx = heap.get(leftIdx).val > heap.get(rightIdx).val ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
} else if (leftIdx < heap.size()) {
targetIdx = cur * 2;
} else {
break;
}
if (heap.get(cur).val > heap.get(targetIdx).val) {
break;
} else {
Num parentVal = heap.get(cur);
heap.set(cur, heap.get(targetIdx));
heap.set(targetIdx, parentVal);
cur = targetIdx;
}
}
return target;
}
}
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution(int[] nums, int deleteCnt) {
MaxHeap2 maxHeap = new MaxHeap2();
IntStream.of(nums).forEach(x -> maxHeap.insert(x));
int cnt = 0;
while (maxHeap.heap.size() != 1) {
Num cur = maxHeap.delete();
if (cnt++ < deleteCnt) {
continue;
}
int oriVal = cur.isMinus ? cur.val * -1 : cur.val;
System.out.print(oriVal + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int nums[] = {3, 0, -2, -5, 9, 6, -11, 20, -30};
int deleteCnt = 1;
solution(nums, deleteCnt);
}
}
20 -11 9 6 -5 3 -2 0

Leave a comment